FUNGI kingdom: characteristics and examples

The Fungi kingdom is a group of organisms composed not only of the mushrooms or mushrooms, if not also for the molds and yeasts. This kingdom is a set of organisms ranging from mushrooms that live at the foot of trees to large forests, to the mold that makes a mandarin inedible, to the yeasts that ferment bread, cheese or the wine. As you can imagine, the living beings that make up the Fungi kingdom are very varied, but what do they have in common? In addition, they are mostly unknown beings, what is the function of fungi, yeasts and molds? Could you name ten organisms of the Fungi kingdom? If you want to know more about Kingdom Fungi: characteristics and examples, We encourage you to keep reading!
Index
- What is the Fungi kingdom?
- Characteristics of the Fungi kingdom
- Examples of organisms from the Fungi kingdom
What is the Fungi kingdom?
The Fungi kingdom is made up of fungi, yeasts, and molds. All of them have very diverse characteristics but, even so, they can be grouped thanks to a unique characteristic common to all of them: they have
chitin cell walls. Like the cells that make up plants, Fungi organisms have a cell wall that lines the cell membrane. The cell wall of plant cells is made of cellulose, while those of Fungi are made of another polymer: chitin. Chitin is a hard compound that forms, among other things, the outer covering of the body of many insects or mollusks.Throughout history, the Fungi kingdom has undergone many changes and the characteristics and examples of organisms that comprise it have not always been the same. In ancient times, this kingdom did not exist: the mushrooms belonged to plant kingdom while yeasts and molds belonged to the protists. Later, researchers began to study the cellular structure of organisms and discovered the chitin cell wall, creating this kingdom. From its creation to the present, many organisms have entered and left this group and the evolutionary and family relationships between them are not well understood.

Image: Answers tips
Characteristics of the Fungi kingdom.
The organisms of the Fungi kingdom are characterized by the following properties:
- They have one chitin cell wall. This is the defining characteristic of the Fungi kingdom as only these organisms have a cell covering made up of this material. This compound gives great resistance to these cells, but also has other characteristics such as being insoluble in water and being widely used for the treatment of wounds, as it forms a film that adheres slightly but resists very well friction.
- They are heterotrophs. Unlike plants, Fungi cannot photosynthesize so they feed on other organisms, such as animals. In general, they are classified according to their diet as: saprophytes (they consume decomposing organic matter), parasites (they consume organic matter from living organisms on which they live) or symbionts (they feed thanks to living organisms, on which they live, but these also obtain some benefit of it).
- Perform external digestion for osmotrophy. Unlike animals, which have an internal digestive system, Fungi organisms do not. Fungi release enzymes to the outside, substances in charge of transforming the most complex molecules (macromolecules) into simpler ones, which they are able to later integrate into your body through phagocytosis or pinocytosis. Some of these enzymes are of great interest to humans since they can be used as antibiotics, mainly to kill bacteria.
- They can live in different types of habitats, although all of them are usually wet or aquatic. Fungi can live in seas or oceans, decaying substances, soils, etc.
- They reproduce sexually or asexually, through spores. Spores are cells with great resistance capacity (at high or low temperatures, low humidity, etc.). To give rise to a complete organism, they may need to join with another (sexual reproduction) or do it on their own, when the environmental conditions are suitable (asexual reproduction).
To know how living beings are organized within the five kingdoms it is important to know characteristics and examples of the Fungi kingdom, which help us to get a clearer idea of what organisms compose it.

Image: Fungi Kingdom
Examples of organisms from the Fungi kingdom.
Within the Fungi kingdom, more than 10,000 species and most are of great ecological, environmental or economic importance to humans. In this section we will see numerous examples of organisms from the Fungi kingdom.
The first great use of the Fungi that we will see will be the feeding. Humans are omnivores and, within our diet we have incorporated the direct consumption of fungi or mushrooms such as Agaricus bisporus (common mushroom) or numerous varieties of species of the genus Amanita. In addition, we have incorporated them into food processing and the food industry: Saccharomyces cerevisiaeAlong with other microorganisms, it is responsible for the fermentation of beer, wine, sake, bread and some industrial alcohols; Yarrowia lipolytica It is used for the industrial scale manufacture of citric acid and Mucor rouxii it intervenes in the maturation processes of some cheeses. Instead, other organisms are harmful to food: Rhizopus stolonifer appears in rotting bread and fruit while Botrytis cinerea produces diseases in grapes.
Another of the great uses of the organisms of the Fungi kingdom is that of the pharmaceutical industry and health. Some microorganisms like Candida albicans, Candida auris, Blastomyces dermatitidis or Coccidioides immitis They produce infections that cause disease, some of which can be very serious. On the other hand, other yeasts and fungi, fundamentally, are a source of health since they are used to research, discover and synthesize antibiotics that help us fight diseases: numerous species of the genre Streptomyces produce antibioticsS. nodosus produces amphotericin B; S. erythreus produces erythromycin; S. rimosus produces tetracyclines and S. mediterranei produces rifampicin, which is used to treat tuberculosis).
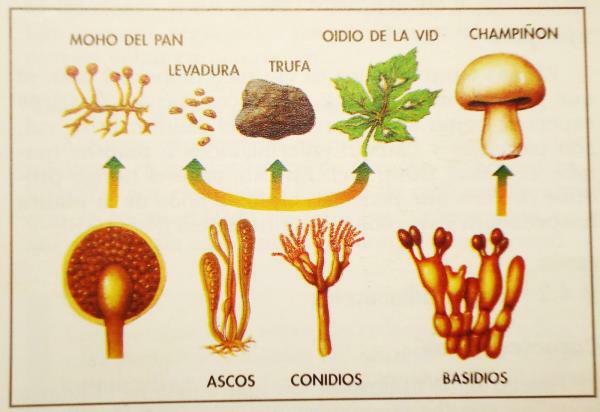
Image: Meanings.online
If you want to read more articles similar to Fungi kingdom: characteristics and examples, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Moore, D., Robson, G. D., & Trinci, A. P. (2011). 21st century guidebook to fungi with CD. Cambridge University Press.
- Siddiqui, Z. A., & Futai, K. (Eds.). (2008). Mycorrhizae: sustainable agriculture and forestry. New Delhi: Springer.
- Uriarte, J. (August 2, 2019). Fungi kingdom. Recovered from https://www.caracteristicas.co/reino-fungi/
- Bioenccyclopedia (s.f) Reino Fungi. Recovered from https://www.bioenciclopedia.com/reino-fungi/
- Argenbio (s.f) Antibiotic-producing microorganisms. Recovered from http://www.argenbio.org/index.php? action = news & note = 237