Learn the main characteristics of modern empiricism
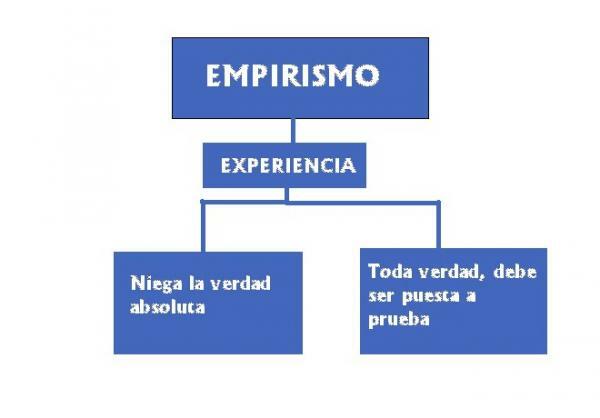
Image: Philosophy
In this new lesson from a TEACHER, we will explain what the modern empiricism and its characteristics, a philosophical doctrine develops during the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. Empiricism is a theory opposed to rationalism that defends that all knowledge comes from experience, from the data of the senses or from reflection. There is no foundation other than observation of the facts, nor do innate ideas exist. The mind is one clean sheet and knowledge, limited. There can be no knowledge beyond sense experience. Would you like to know more about features of themodern empiricism? We started!
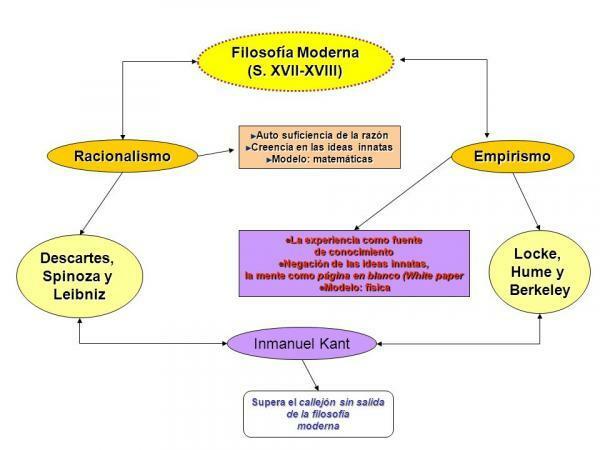
The empiricismmodern developed during the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, its main representatives are the British Locke, Berkeley Y Hume, and against the rationalism of Descartes, Spinoza Y Leibniz, he defends that all knowledge, all ideas come from sensible experience. There are no innate ideas. Reality depends on the senses. There can be no knowledge outside of experience. Rationalists, on the other hand, affirm the existence of innate ideas and of a reality independent of the senses.
At the end of the 18th century, Immanuel Kant, he overcomes both theories with his philosophical criticism, stating that there are two types of knowledge, one that comes from experience, from the data of experience and is the sensitivity, and another that collects information from the data of the senses, and is the understanding. The understanding, part of the data of the senses but does not depend on the experience. Knowledge, for Kant, is the representation of an object that a subject builds from sensitive perception. This is a true revolution in its time and is known by the name of Copernican Twist.
Objects are therefore given to us through sensitivity and it is the only one that provides us with intuitions. By means of the understanding, the objects are, instead, thought and from him the concepts proceed. Immanuel Kant. Critique of Pure Reason, Transcendental Aesthetics. (Alfaguara, Madrid 1998, 15th ed, page 65)
The fundamental theme of the empiricist philosophers will be that of origin, limit and validity of knowledge, which for this current, is found in experience. Human knowledge begins in experience, and there is also its limit, since outside it, there can be no knowledge, and it is also its criterion of validity.
The empiricist experience
Well, the experience can come from the outside, from the data of the senses, that is, from the sensitive perception. But it can also come from within, or what is the same, from abstraction, reflection or mental perception.
Knowledge, for empiricists, They are ideas, not sensible objects, a concern that they share with the rationalists, with the difference that the former deny the existence of the innate ideas contained in reason. Likewise, they deny that deductive knowledge is valid for the study of natural sciences, required by the inductive method, the deductive method being restricted to the field of logic and math.
Kant, I.Critique of Pure Reason, Transcendental Aesthetics. Alfaguara, 1998
Hume, D. Treat of human nature. Tecnos, Madrid 2005
Locke, J. Essay on Human Understanding. Economic Culture Fund, 1999