Characteristics of dialectics in philosophy

In this lesson from a PROFESSOR we explain the main characteristics of dialectics, a branch of philosophy that studies the relationships between pairs of opposites. Plato, Hegel or Marx, have wanted to explain the nature of things, based on their opposites, and from that contradiction, from that denial of concepts, new ones arise, in an overcoming of the previous ones. A thesis (statement), necessarily follows from his antithesis (negation), which implies a synthesis (overcoming). Because each solution always contains a new problem. If you want to know more about the characteristics of dialectics in philosophy, continue reading this article by a TEACHER.
Index
- 7 characteristics of dialectics
- Dialectic in Greece
- Hegelian dialectic
- Materialist dialectic of Marx and Engels
7 characteristics of dialectics.
The dialectics It is that branch of philosophy that tries to give an explanation of the world, of reality, of history, based on the relationships between
pairs of opposites. For a better understanding of the term, here is a summary with the most outstanding characteristics of dialectics in philosophy:- It is a concept that changes over time, although its essence is the same, the relationship between pairs of opposites.
- In its origins it was understood as a method to dialogue.
- In order to Hegel, the contradiction is precisely what allows the birth of new concepts.
- The posture of Marx is materialistic when applied to story.
- Reality is understood as circular process, dynamic and in this process there are three moments, starting from the principle of contradiction.
- In order to Fichte, these three moments would be: thesis, antithesis, synthesis.
- According Hegel, The three phases of the dialectical process are: abstract, negative, concrete.
Dialectic in Greece.
Plato was the creator of Dialectical methodin philosophy and all dialogue between two opposites, it is considered dialectical. It is about discussing an issue in order to get to the truth. But the true father of Western dialectics was Heraclitus of Ephesus, called "The dark one", considering that the essence of things is in change and that contradiction is a dynamic and not static process. All things, therefore, are opposed to one another, and in that opposition, each term is the negation of the other.
Thus, for Heraclitus, “everything changes, nothing remains" and the "war is the father of all things”, Because war is nothing more than contradiction, the struggle between opposites.
Heraclitus was not an ordinary philosopher and he himself denied it by stating at the same time that
“Nor it is possible to go down to the same river twice because those who go down are submerged in always different waters in its incessant flow" Y "We go down and do not go down to the same river, we are and we are not".
This means that in permanence there is change and in change there is permanence.
Plato's Dialogues offer an application of the dialectical method but also, in Gorgias, Republic VI and VII and Theaetetus, explains what the process consists of.
Platonic dialectic
From Plato one could perceive the formal beginnings of this notion. Plato's dialectical method born from Socratic maieutics, in order to achieve knowledge and the "Idea of Good". For Plato, from the relationship between pairs of opposites, one can arrive at the truth.
Finally, do not forget that for AristotleThe search for first principles is a dialectical process, since, although it is not possible to demonstrate them, it is possible to deny them with another argument.
Hegelian dialectic.
We continue this lesson on the characteristics of dialectics in philosophy, now meeting another of the great philosophers. In order to Hegel, the development of thought does not occur if it is not from the contradiction, of the relationship between opposite pairs. It is from the contradiction that ideas are born.
In the dialectical process, there are three phases:
- Abstract or Thesis: formulation of an idea
- Negative or Antithesis: denial of that idea
- Concrete or Synthesis: overcoming the previous two with a new idea
When an idea arises, new ones immediately appear that contradict each other, but in the end, a new one ends up emerging that comes to overcome the contradiction between the first two.
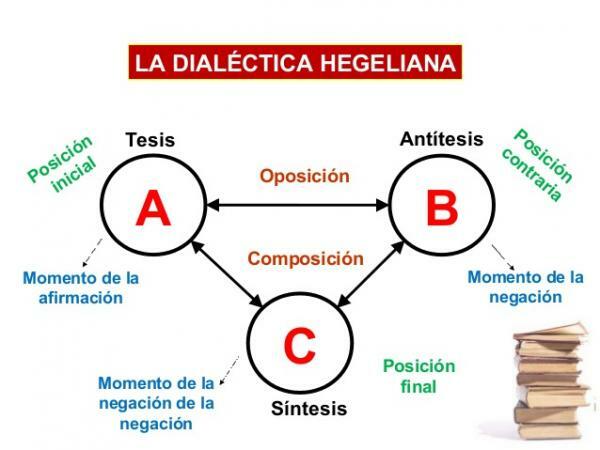
Image: Youtube
Materialist dialectic of Marx and Engels.
The Materialist Dialectic from Marx and Engels was born from the Hegelian dialectic, but applied to history, understood as the eternal class struggle. We have an example in the opposition that exists between the capitalist and the worker, a contradiction that will have to be overcome.
Laws of materialistic dialectics
- Law of unity and fight of opposites.
- Law of the transit of quantitative changes in qualitative.
- Law of denial of denial (overcoming)
Principles of the materialist dialectic
- Principle of constant change
- Principle of reciprocal action
- Principle of unity of opposites
- Principle of quantitative changes and qualitative jumps
“This is the eternal cycle in which matter moves, a cycle that only closes its trajectory in periods for which our terrestrial year cannot serve as a unit of measurement, a cycle in which the time of maximum development, the time of organic life and, even more, the time of The life of conscious beings of themselves and of nature, is as sparingly measured as the space in which life and self-consciousness exist; a cycle in which each finite form of existence of matter - whether it is a sun or a nebula, an individual animal or a species of animals, the combination or the chemical dissociation - is also temporary and in which there is nothing eternal except matter in eternal movement and transformation and the laws according to which it moves and moves. transform”.
Friedrich Engels, Dialectic of nature.
If you want to read more articles similar to Characteristics of dialectics in philosophy, we recommend that you enter our category of Philosophy.
Bibliography
Détienne, M. The Masters of Truth in Archaic Greece. Ed. Sixth Floor. 2005.
Marx, K and Engels, F. The Holy Family or Critique of Criticism. Ed. CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform, 2016.
Engels, F. Dialectic of Nature. Ed. Greenbooks editore, 2019.
Hegel, G, W, F. The Phenomenology of the Spirit. Ed. Economic Culture Fund, 2017
