What is a NULL angle

In this lesson from a PROFESSOR we present you what is a null angle, characteristics and examples. To begin, we are going to review what an angle is, what are the types of angles that exist and their elements, and then delve into the concept of angles. null angles. Then we will see its characteristics, the difference with the flat angle and some examples.
To understand what a zero angle is, we must first review some necessary concepts for it. In geometry, an angle is the part of the plane that is formed from two lines, half lines or segments that have a common origin, or two lines that intersect to form 4 angles.
The main elements of angles are:
- sides: are the half lines that form it
- Vertex: the point where the half lines meet
- Opening: amplitude or opening formed by half lines, this is measured in degrees or radians
types of angles
There are different types of angles, such as:
Convex angles are those angles formed by two lines, half lines or segments whose amplitude or opening does not exceed 180° sexagesimals. There are three types of angles:
- acute angles, are those that measure less than 90° but more than 0° sexagesimal
- right angles, are those that measure exactly 90° sexagesimal and their sides are perpendicular to each other.
- obtuse angles, are those that measure more than 90° but less than 180° sexagesimal
- There are also the flat angles, which are those angles formed by two rays that measure exactly 180° sexagesimal. That is, its amplitude or opening is 180° sexagesimal.
- concave angles, whose opening measures more than 180° but does not exceed 360° sexagesimals.
- The full angles are those that accurately measure 360° sexagesimals
- And finally we have the null angles who are those who They measure 0° sexagesimals.
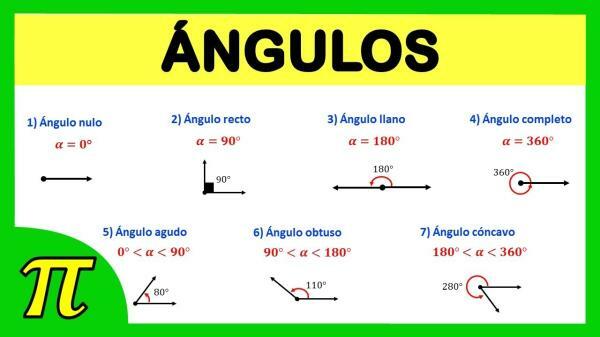
For geometry, the null angles are those angles whose opening or amplitude does not exceed 0° sexagesimal, that is to say, that in reality do not have opening some. The rays that form the angle are coincident, that is to say that there is no distance between them that separates them and therefore the amplitude does not exist.
Due to this, it can be thought that the null angle is an angle that does not exist directly since only a ray can be visualized when seeing it. But it is important to know this type of angles since the mobile angles could close to reach 0° sexagesimals.
Although its concept sounds very simple, these angles they are very useful in many applications both in engineering and physics, as well as navigation and design in general.
So we can say that a zero angle is the one that is found between two coincident lines, rays or segments, and that they share all their points in common, therefore there is no measurable openness between them.

In daily life, although we do not notice it, we have many examples of null anglesLet's see some:
- A compass It is made up of two parts whose tips have a needle and a pencil lead. When the compass is closed, both parts are in contact so they form a zero angle of 0°. Although the sides of the compass are not specifically overlapping, the separation is minimal, so we can consider it as a valid example.
- A scissors. When the sides that form the scissors are completely closed, they overlap and form an angle of 0°, therefore a zero angle as well.
- A fan, when a fan is fully open we can visualize an obtuse angle, that is, an angle greater than 90° sexagesimal, but less than a flat angle. When completely closed, the ends of the fan overlap, thus forming an angle of 0° sexagesimals, that is, a zero angle.
- When a vehicle travels on a highway straight in one direction and there is another vehicle that left from the same starting point and takes the same route, we can say that their trajectories form a zero angle. This type of example is widely used in exercises or problems to be solved in physics, since speed, trajectory and acceleration are vectors.
- A stair. When the sides of a ladder open up, they form an angle greater than 0° but less than a right angle. When the ladder is closed, its sides are coincident and thus form a zero angle.
- the hands of a clock They form all kinds of angles, but when the two hands coincide at the same number, for example 15:15 or 14:10, the hands coincide thus forming a zero angle.