GEOMETRIC bodies: classification and elements
In this one-TEACHER lesson we are going to study the geometric bodies and their names. First we are going to start with the origin and meaning of the name, why they are called bodies geometric figures, we will review the geometric figures and then see geometric bodies and know their characteristics.
Index
- Origin of geometric bodies
- What is a geometric figure?
- What are geometric bodies and their names
- Classification of polyhedra
- Regular polyhedra: names and classification
- Classification of irregular polyhedra and their names
- Classification of round bodies
Origin of geometric bodies.
It is important to know the etymological origin of the words to better understand their meaning. The origin of the two words that form the term "geometric body” is as follows:
- Body: is derived from Latin. It comes from “corpus” and can be translated as “trunk”.
- Geometric: Its origin comes from the Greek. It is formed from three clearly differentiated elements: “geo” means “earth”; "metron" synonymous with "measure", and the suffix "-ico", is used to indicate that it is "relative to".
A geometric field is an element that has three dimensions. and these are height, width and length. It could be said that it is a kind of geometric figure.
What is a geometric figure?
The geometric figures They're a visual and functional representation of a non-empty and closed set of points in a geometric plane. By this we mean that they are figures that delimit flat surfaces by means of a set of lines or sides that join their points in a certain way. According to the order and number of these lines we will see different figures.
The matter that is worked on in geometry are precisely these geometric figures. Geometry is the branch of mathematics that studies planes, representations, and the relationships between the different shapes that can be imagined with them. They are those abstract objects that determine the way we understand the universe.
Classification of geometric shapes
Geometric shapes can be classified according to shape and number of sides, or based on the number of dimensions they represent.
- dimensionless figures. It has 0 dimensions and refers to the point.
- Linear figures. It has a dimension and they are lines with a certain orientation and route, that is, they are straight and curved.
- Plane figures. They have two dimensions and are figures that lack depth. They have a length and a width, and are polygons, planes, and surfaces.
- Volumetric figures. It has 3 dimensions and are figures that add depth and perspective. They are considered geometric bodies, such as polyhedrons and solids in revolution.
- N-dimensional figures. They have n dimensions, that is, more than 3 dimensions, and they are theoretical abstractions.
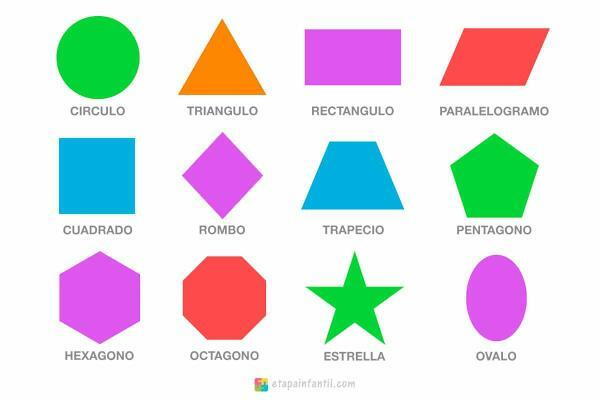
Examples of geometric figures
- triangles
- Squares
- diamonds
- circumferences
- ellipses
- pyramids
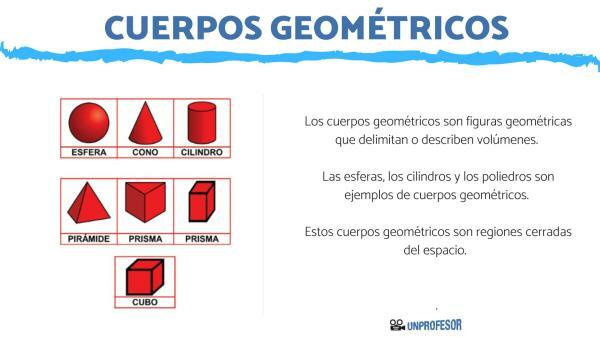
What are the geometric bodies and their names.
The geometric bodies are geometric figures that delimit or describe volumes. Spheres, cylinders and polyhedrons are different geometric bodies. These geometric bodies are closed regions of space.
The geometric bodies are divided into two large groups, some are the polyhedra and the others are round bodies. Polyhedrons are those delimited by flat surfaces. And the round bodies are those delimited by curves.
Example
Let's see an example to understand more easily the meaning of a geometric field.
A square is a quadrilateral: a geometric figure with four sides. A cube, on the other hand, is a polyhedron with six square faces, that is to say, a geometric body that has height, width and length.

Classification of polyhedra.
The polyhedra are geometric bodies limited by flat surfaces.
The geometric bodies occupy a place in space and, therefore, it means that they have volume. If their faces are flat, they are called polyhedra. Among them we can distinguish regular polyhedra and irregular polyhedra.
The polyhedra have the following items:
- Faces: They are the polygons that delimit the polyhedron.
- Edges: They are the edges of the faces.
- Vertices: They are the points where three or more edges meet.
- Plane angles: Formed by two converging edges.
- Dihedral angles: Formed by two adjacent faces.
- Polyhedral angles: Formed by three or more faces that converge at a vertex.
- Diagonals: there are diagonals that join two non-consecutive vertices of the same face and diagonals that join vertices of different faces.
Classification of polyhedra
according to their angles
- concave
- convex
To know if a polyhedron is concave or convex, its faces are prolonged, in the case in which any of the extensions pass through the interior then it will be concave, if on the contrary it does not happen it will be convex.
according to the shape of their faces
- Regular polyhedra, where all their faces are regular polygons equal in both shape and size.
- Irregular polyhedra, contrary to regular polyhedra, that is, if the above does not occur.
According to the number of faces
- Tetrahedron, or four-sided polyhedron
- Pentahedron, five-sided
- Hexahedron, Exahedron, or Cube, six-sided
- Heptahedron, seven-sided
- Octahedron, eight faces
- And successively...

Regular polyhedra: names and classification.
Only There are five regular polyhedra. They are the simplest and are formed from a single regular polygon.
- tetrahedron. It has four faces that are equilateral triangles, four vertices, and six edges. It is the geometric body with the smallest volume compared to its surface.
- Cubeeither hexahedron. It has six faces that are square, eight vertices, and twelve edges.
- Octahedron. It has eight faces that are equilateral triangles, six vertices, and twelve edges.
- Dodecahedron. It has twelve faces that are regular pentagons, twenty vertices, and thirty edges.
- icosahedron. It has twenty faces that are equilateral triangles, twelve vertices and thirty edges. It is the geometric body with the greatest volume in relation to its surface.

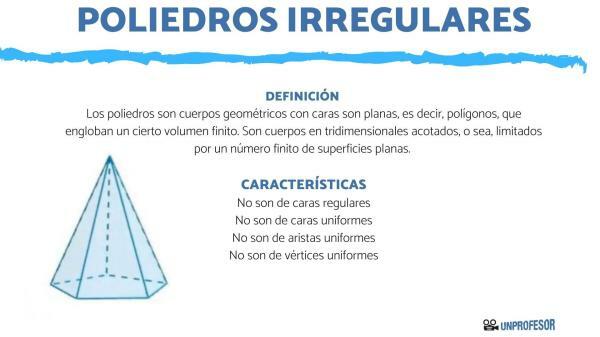
Classification of irregular polyhedra and their names.
The classification of irregular polyhedra It is simple, since there are only two large groups. prisms and pyramids.
prisms
They are those polyhedra that are formed by two equal and parallel faces that we call bases and by several rectangular lateral faces. The number of side faces will depend on the number of sides the base polygon has.
- If its base is a regular polygon then we will call it a regular prism.
- If instead the lateral edges are perpendicular to the base, we will call it a right prism.
pyramids
They are those polyhedrons that end in a vertex resting on their base, so their lateral faces are going to be triangles. They are prisms with a single base.
- If its base is a regular polygon then we will call it a regular pyramid.
- If the line that joins the vertex with the center of the base of the polygon coincides with the height of the pyramid, then we will call it a right pyramid.
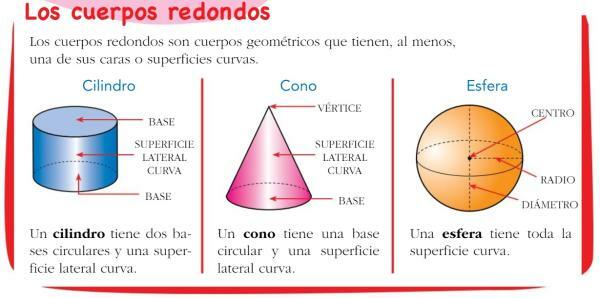
Classification of round bodies.
Round bodies are formed when we rotate a certain figure around an axis, that is to say, of a straight line. The simplest and most well-known round bodies are the cylinder, the cone and the sphere.
Cylinder
Round body that is formed when we rotate a rectangle around one of its sides.
The elements that compose it are:
- axis of rotation
- generatrix
- height
- radio
Pussy
Round body that is formed when we rotate a triangle around one of its legs.
The elements that compose it are:
- axis of rotation
- generatrix: hypotenuse of the triangle
- height
- radio
Sphere
Round body that is formed when we rotate a circle around a diameter.
The elements that compose it are:
- radio
- diameter
If you want to read more articles similar to Geometric solids: classification and elements, we recommend that you enter our category of Geometry.



