What is a RIGHT angle

A right angle is a type of angle that measures exactly 90 degrees. In unProfesor we tell you in detail and we leave you with examples and solved exercises so that you can practice at home.
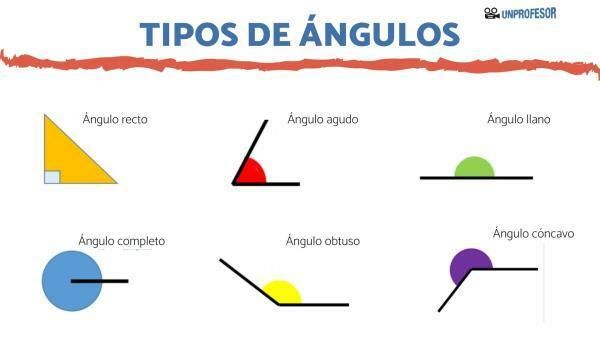
In this new lesson we will look at the right angle and examples. We will start with the concept of angle and its types, we will continue with the right angle and examples to end with some exercises on the subject.
In mathematics, more specifically in geometry, the concept of angle.
An angle is the part of the plane that is included between two lines or rays., which are called "sides" that start from a common point called origin or vertex. These sides and vertices generate an opening which is measured in sexagesimal degrees or radians and which we call angle.
In other words, we can say that the angles are those parts or regions in the plane that are formed from the union of two lines or half lines that share a point or vertex.
angle measurement
The angles are measured, as we said before with the sexagesimal system.
Its measurements are in degrees, minutes and seconds. Degrees equal 60 minutes while minutes equal 60 seconds. The complete rotation of an angle measures 360 sexagesimal degrees, which is equivalent to the total rotation of a circle.We can also measure angles with the radian system, where a complete circle is measured with 2π radians.
A right angle is an angle that is formed between two lines and a vertex in common whose measure is exactly 90° sexagesimals or π2 radians.
We can say that with the sum of two consecutive right angles we obtain a flat angle, which we remember measures exactly 180° sexagesimals. In turn, four consecutive right angles to each other form a complete turn, that is, they add up to 360° sexagesimals.
In this lesson of a Teacher we discover the different types of angles that exist.

In everyday life, we can see many examples of right angles, such as the junction between the floor and the wall or the junction between the wall and the ceiling. A rectangular-shaped piece of furniture, the corners of a television, etc.
In geometry, we can see the following examples of right angles:
- Perpendicular straight lines: When two lines are perpendicular to each other, they form four right angles.
- Square: All the interior angles of a square measure exactly 90° sexagesimal. The sum of the four interior angles is equivalent to 360° sexagesimals. In turn, when the diagonals of a square intersect, they also form right angles.
- Rectangle: In the same way as with the square, the interior angles that form it each measure exactly 90° sexagesimals.
- Right triangle: it is named in this way, for having one of its interior angles whose measure is exactly 90° sexagesimals. The remaining two measure 90° added to each other, since the total sum of the three interior angles of any triangle must measure 180° sexagesimals. This type of triangle is used a lot in mathematics. Its most frequent use is with the Pythagorean theorem.
- Diamond: The diagonals of the rhombus form angles of 90° sexagesimal or right when crossing.
- rectangle trapezoid: two of its interior angles each measure exactly 90° sexagesimals, that is to say that two of its angles are right.
Exercise 1
1) Answer True or False
- The interior angles of a right isosceles triangle that do not measure 90° each measure 30 sexagesimal degrees.
- The interior angles of a square add up to 360° sexagesimals.
- Two consecutive right angles add up to 190° sexagesimals.
- The diagonals of a rectangle form angles of 90° sexagesimal each.
- The diagonals of a rhombus form angles of 90° sexagesimals.
Solutions
- Fake. The remaining angles measure 45° each, since the interior angles must measure 180° sexagesimals in total, and one of them measures 90° sexagesimals because it is right.
- TRUE. The interior angles measure 90° each, so they add up to 360 sexagesimal degrees.
- Fake. They add up to 180° sexagesimals.
- Fake. The diagonals of a rectangle do NOT form right angles.
- TRUE. Each intersection forms a right angle.
Exercise 2
2) Choose the correct option
Two complementary angles sum:
- 90°
- 180°
- 360°
The straight angle measures exactly:
- 45°
- 180°
- 90°
The diagonals of a square form:
- 5 90° angles
- 3 90° angles
- 4 angles of 90°
The sum of four right angles is equal to:
- 180°
- 270°
- 360°
A null angle is equal to an angle of:
- 50°
- 0°
- 90°
Solutions
- Two complementary angles add up to 180° sexagesimals
- The straight angle measures exactly 180° sexagesimals.
- The diagonals of a square form 4 sexagesimal 90° angles.
- The sum of four right angles is equal to 360° sexagesimals.
- A null angle is equal to an angle of 0° sexagesimals.
If you liked this lesson from a Teacher, don't forget to share it with your classmates. You can keep browsing the web to find more content like this.