How plants feed

All living beings need to incorporate materials from the environment in order to survive. Our body needs to generate energy so that we can carry out all daily activities, from walking, thinking, breathing, brushing our teeth to sleeping. We obtain this energy from the food that we take in through our mouths and from the oxygen that we inhale from the air through our nostrils. This way of obtaining energy is particular to animals. But have you ever wonderedhow do plants eat? In this lesson of unTEACHER.com we will tell you how plants obtain energy.
Index
- The function of nutrition in plants
- What do plants need to produce their food?
- The process of photosynthesis
- The respiration of plants for their food
- Disposal of plant debris
- Other types of plant nutrition
The function of nutrition in plants.
All living beings have various characteristics in common: they are formed by cells and have the same life stages, they are born, develop and grow, reproduce and die. In order to grow, living organisms need energy and construction materials, with this they repair their tissues, renew and increase their number of cells. This
function of living beings is the nutrition function. Nutrition is the process by which organisms they obtain the matter and energy to build their own structures and be able to carry out their vital functions.As mentioned above, animals incorporate food and oxygen, generating energy to grow and carry out their activities. We can notice with the naked eye that plants do not have the same characteristics as animals. We know that plants do not have a mouth through which to incorporate food and they do not have nostrils to breathe air. So how do these organisms generate energy?
The main difference between animals and plants is that plants have the ability to make their own food without incorporating it from the middle. Animals, on the other hand, incorporate their construction materials using other living beings, their derivatives (such as fruits) or decomposing matter as food.
There are two forms of nutrition: autotrophic and heterotrophic. Plants are autotrophic organisms or producersThis means that they produce their own food. On the other hand, the form of nutrition of most animals is heterotrophic, this means that they are consumers, they do not produce the food they consume.
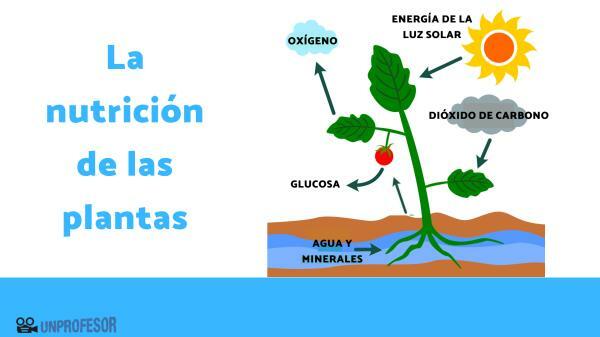
What do plants need to produce their food?
Unlike animals that must obtain their food using various hunting or search techniques, plants simply need to get some sun, capture carbon dioxide from the air and absorb water and mineral salts through the roots. Plants have different structures and specialized cells to be able to capture solar energy, to to be able to incorporate the gases from the air into your body and to be able to collect water and minerals through your estate.
The process of photosynthesis.
The process of obtaining energy from plants is called photosynthesis. From the energy of the sun, carbon dioxide, mineral salts and water form glucose, which is food, and produce oxygen as a waste or result.
Where does photosynthesis occur?
The plants have the particularity of being of green color. The pigment that gives them this color is called chlorophyll. chlorophyll It is found in all plant cells in a structure called chloroplast. Chlorophyll has the ability to absorb sunlight or artificial light.
The process of photosynthesis for plant nutrition
Let's see step by step how plants produce their own food thanks to photosynthesis:
- The soil is composed of various minerals and has some moisture. The roots of plants are considered specialized organs for the soil nutrient uptake, only the minerals that are dissolved in the water are those that reach the plant through the roots. Through the root absorbing hairs water enters the plant with minerals from the soil.
- The mineral salts and the water form the so-called raw sap, which must travel inside the stems of the plant through woody vessels (similar to the blood vessels of animals) until it reaches the leaves where photosynthesis takes place.
- Plants also breathe exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide with the atmosphere. To carry out this gas exchange they have specialized structures called stomata, are found in stems and leaves of plants and form a kind of pore through which gas exchange takes place. for it to happen photosynthesis, carbon dioxide enters through the stomata to reach each plant cell and, finally, the chloroplasts. Oxygen is produced as waste in photosynthesis and is released into the environment through stomata. Through the stomata, water vapor is also lost to the environment, so the plant must regulate through them the entry and exit of gases and also the loss of water to generate a balance. When there is not enough water in the environment to absorb through the roots, the plant must keep the stomata closed for a longer time to avoid dehydration.
- The products obtained from photosynthesis are collectively called elaborated SAP, is a mixture of sugars, amino acids, salts and water. The main place of production of processed sap, where photosynthesis occurs mostly, is in the leaves of the plants, this sap is transported to the places of energy consumption, which are usually stems and roots (growing organs) or fruits and seeds (storage organs).
stages of photosynthesis
- Light phase: sunlight stimulates chlorophyll and breaks down water molecules, releasing oxygen into the atmosphere.
- Dark phase: It does not require sunlight, water and carbon dioxide come together to form organic matter (glucose) that will be the plant's food.
Here you can read about The plants' photosynthesis and here below you can see a video about the cyclic light phase of photosynthesis.

The respiration of plants for their food.
Until now we have told you how plants feed or how they generate organic molecules or glucose through photosynthesis to feed themselves. Up to this moment the plant has done nothing more than consume energy to manufacture its food, but as mentioned above, all living beings need to generate energy to perform their functions vital. You will now ask yourself how do plants release or generate this energy? The processes of obtaining energy in living beings are carried out from the degradation of organic molecules, this process is known as cellular respiration. Let's see what this is about.
Cellular respiration is a process that needs oxygen. Oxygen breaks the bonds of organic molecules and this produces the release of energy that will be used for all vital activities. This process occurs in a cell organelle called mitochondria. This implies that the plant, in addition to eliminating oxygen in the photosynthesis stage, must also consume it in order to carry out the cellular respiration process. Oxygen, like carbon dioxide, enters and leaves the plant through the aforementioned pores, known as stomata.
in plants, glucose generated in photosynthesis is stored as starch. When the plant needs energy, the starch is broken down into its glucose units to be degraded in the process of cellular respiration and thus be able to get power. Therefore, plants are organisms that have two types of organelles in their cells: chloroplasts and mitochondria, in the first photosynthesis occurs and in the second the cellular respiration.
We recommend you read this other lesson on plant cell function.
Disposal of plant debris.
Living organisms, in these processes mentioned so far, also produce waste or products that are harmful to the body.
In the case of plants, the waste produced in photosynthesis is used in cellular respiration. Plant waste is excess carbon dioxide, oxygen, and water in the form of steam. In addition, some plants produce certain waste substances or secretions.
For example, pine trees produce resin in their bark, this substance has a defense function, it closes wounds in the trunk, preventing insects that feed on the wood from entering. The essences and nectar produced by some flowers have the function of attracting pollinating insects in order to spread. Latex is produced by some plants, it is a milky and sticky liquid that contains sugars and toxic substances to defend the plant from being eaten by herbivorous or omnivorous animals.
Other types of nutrition in plants.
There are plants that have been capable of developing other forms of nutrition: parasitic, predatory or carnivorous and symbiotic plants. Through these mechanisms they manage to obtain nutrients from other living beings.
- parasitic plants They are the ones that carry out photosynthesis, but they do not take nutrients and water from the soil, but rather they obtain it from the plant they parasitize. Other parasitic plants do not carry out photosynthesis and suck the sap produced directly from the plant they parasitize. In both cases, the plants that carry out parasitism harm the host plant.
- carnivorous plants They photosynthesize, but complete their diet by catching certain insects. Here you can meet The parts of a carnivorous plant.
- symbiotic plants they associate with other organisms to obtain benefits. For example, mycorrhizae are associations of fungi with the roots of plants, both benefit, the fungi provide minerals to the plants and obtain organic compounds in return. On the other hand, we can also mention legumes, the roots of these plants have protuberances where a type of bacteria, these bacteria are capable of capturing a mineral from the air and provide it to the plants, in turn the bacteria obtain sugars from the plant.
If you want to read more articles similar to How plants feed, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- CurtisH., BarnesN. S. 2004. "Biology", sixth edition in Spanish. Panamerican medical editorial. Buenos Aires, Argentina.
- Chapter 11. "The process of nutrition in plants". Page 242 to 258. Publishing Mc Graw Hill.

