Vulgarism: definition and examples

When you use speech in a informal settingIt is likely that some vulgarism will slip into your speech. It is an incorrect way of using the Spanish language and it is used in a communicative environment colloquial, therefore, is not so much related to the knowledge of the language as to the context of the communication. In this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to show you the definition of vulgarism with examples so that you understand well what this linguistic phenomenon consists of, which is so present when using the language in informal and familiar contexts.
The language is a living system since, in addition to the standardized and normative language, the speakers are forming their own language and that may be different from the one stipulated. It is then that words such as vulgarisms, expressions that are used within the informal or colloquial language So what does not respect the regulations stipulated by the academy. These expressions can refer to syntax, phonetics, or morphology.
However, it is important to note that some words that were formerly considered vulgarisms are now accepted. This may happen because the Royal Spanish Academy is open to incorporate linguistic changes and developments that are being important within society. As we have said, we are facing a living system that is formed thanks to the use of speakers.
We should not confuse vulgarism with a lack of knowledge of the language because it is not always a sign that reflects the ignorance of the speaker. Simply, there may be vulgarisms that depend on the region in which the speaker resides and where there is influence of expressions from other languages. This would be the case of the use of words like "recently" in Latin American dialects, an expression that is influenced by the English of North America.
Therefore, in the definition of vulgarism we must indicate that it is an expression that is used in the informal registrationSo what does not respect the rules of the standard language. It does not imply that the speaker does not have knowledge of good linguistic use, but that it is simply the way they use when expressing themselves in a familiar or close environment.

Image: Slideshare
After we have explained what vulgarism is, it is important that we finish completing this lesson providing examples of vulgarisms that can help us to better understand what this phenomenon. Here is a selection of examples of vulgarisms so you can understand what they are:
- * Maybe (the correct thing is "Maybe")
- * Aiga (instead of "haya")
- * Andé (instead of "I walked")
- * Ai (instead of "there" or "there")
- * Aúja (instead of "needle")
- * Butcher shop (instead of "butcher shop"
- * Tas (instead of "you are")
- * Toy (instead of "I am")
- * You came (instead of "you came")
- * Difference (instead of "difference")
- * Diabetes (instead of diabetes)
- * Doctor (instead of "doctor")
- * Scrub (instead of "scrubbing")
- * Ginnasia (instead of "gymnastics")
- * Grabiel (instead of "Gabriel")
- * Güeno (instead of "good")
- * Indiosyncrasy (instead of "idiosyncrasy")
- * Siñor (instead of "sir")
- * Istituto (instead of "institute")
- * Sugar (instead of "sugar")
- * Millet (instead of "my son")
- * Older (instead of "older")
- * More better (instead of "better")
- * Naide (instead of "nobody")
- * Onde (instead of "where")
- * P'aquí (instead of "for here")
- * Feet (instead of "feet")
- * Remember (instead of "remembering")
- * Semos (instead of "we are")
- * Tiatro (instead of "theater")
- * Yerna (instead of "daughter-in-law"
As you can see, vulgarisms affect both phonetic uses, morphology or the syntax of the language.
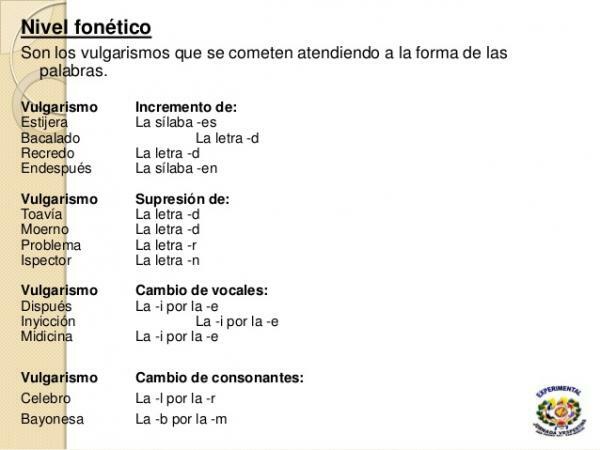
Image: Slideshare
Now that you know what vulgarism is and some examples, it is likely that a question has arisen in your mind: What is the difference between vulgarism and barbarism? Although both phenomena may be similar, the truth is that we are facing two different forms. Here we analyze them:
- Barbarism: these are errors that appear when a word is mispronounced, misspelled or a word that is not used in the communicative act is used. Normally it is related to the speaker having little knowledge of the language.
- Vulgarism: It occurs in colloquial speech, therefore, we find that they are rather incorrect expressions of the language that are used in the informal register. It is not so related to academic training but rather to the communicative context, that is, a university person may use vulgarisms when speaking with his family, not for lack of knowledge, but for the language register you employ.



