2 parts of the central NERVOUS system and their functions

He nervous system of our body It is responsible for transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body, including internal organs. This system is very important, since it allows us to move, breathe, think, see, etc. The nervous system is made up of two main parts: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system.
In this lesson from a TEACHER, we are going to explain to you in detail what are the parts of the central nervous system, so you can see how this important system of the human body works. Let's go there!
Index
- What is the central nervous system
- What are the parts of the central nervous system
- Diseases in the central nervous system
What is the central nervous system.
As we mentioned above, the nervous system has two main parts. One of them is the Central Nervous System, which is composed of the brain and the spinal cord and the other is the peripheral nervous system, which is made up of all the nerves that branch from the spinal cord and extend to all parts of the body.
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system that coordinates all the bodily processes of our body. It controls the vital processes of our body, such as breathing, walking, reacting to an emergency, etc.
At unProfesor we discover what the nervous system organs.
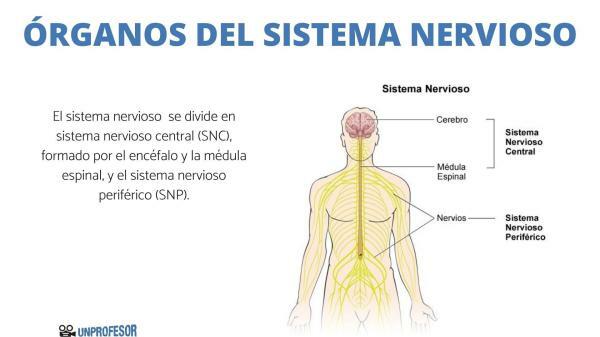
What are the parts of the central nervous system.
The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord. We explain a little more about the parts of the central nervous system.
The brain
This part of the central nervous system controls emotions, memory, thinking, touch, vision, breathing, hunger, and motor functions. How many things! The brain is made up of three main regions:
- Brain: This is the largest part of the brain. Its largest part is the cerebral cortex and is known as the "gray matter." This cortex has 4 areas called lobes, which are those that act to generate the personality and all the knowledge of a specific person. The four lobes are: the central lobe (planning, imagination, decision making, reasoning), the parietal lobe (touch, taste and temperature), the temporal lobe (allows us understand sounds and language, recognize objects and faces, create memories) and the occipital lobe (processes the visual information that comes from the eyes, so that we understand what we are seeing).
- The brainstem: It connects the brain to the spinal cord and works to control and coordinate messages to and from the brain. Additionally, this is the part in charge of controlling functions of the body that we never think about, such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, swallowing and digestion.
- The cerebellum: It is also known as "the little brain" as it looks like a small-scale version of the brain. It is responsible for controlling balance, movement and coordination.
These parts are responsible for processing the information that comes from the body and create commands that indicate each of the tissues in our body. how they should respond to stimuli. These stimuli can come from the external environment, but also from ourselves.
Spinal cord
The spinal cord It is another part of the central nervous system. It is the continuation of the brain stem and its main function is transfer information between the brain and the rest of the body. It has the ability to generate commands, but only to control involuntary actions, that is, reflexes. If we put our hand in the fire, for example, it is the spinal cord that activates the reflexes that give us the order to remove our part of the body from that source of heat.
The brain and spinal cord are very important parts of our body, but also very delicate. That's why they are well protected! The brain is protected by the bones of the skull and the spinal cord by a series of bones intertwined in the shape of rings, called vertebrae, do they sound familiar to you?
In addition, they have another layer of protection which are the membranes called meninges and the cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid flows through the empty spaces in the brain (called ventricles) and around the spine. Its main function is protect the central nervous system, provide it with the nutrients it needs and remove waste.
Here we discover the differences between the central and peripheral nervous system.

Diseases in the central nervous system.
Now that you know the parts of the central nervous system, let's learn about the main conditions. Although the organs of the central nervous system are very well protected, There are diseases that attack it and deteriorate some of the vital functions, like breathing, swallowing or sleeping. These diseases can also alter cognitive functions such as the ability to memorize, language, visual stimuli, hearing, touch, etc.
These pathologies are known as neurological diseases and these are some of the best known. Remember that, contrary to what you may believe, these diseases do not have their origin in a malfunction of the body, but rather in the central nervous system:
- Alzheimer's: This pathology is degenerative and consists of the slow destruction of neurons. This is the most common type of dementia and the most obvious symptom that occurs is memory loss.
- Multiple sclerosis: It is a disease that affects the brain and spinal cord. Demineralization of the sheaths that protect the nerves does not allow electrical impulses to reach and from the brain. This causes symptoms such as weakness in the limbs, blurred vision, dizziness, fatigue, tingling sensation, etc.
- Parkinson's: This disease begins in the nerves located in and around the intestine and nose, but later spreads to the brain, affecting the central nervous system. It directly affects muscle control and movement.
We hope that this lesson has been able to help you understand a little better the parts of the central nervous system and the importance it has in the functioning of our body. If you want to continue learning more about the secrets hidden in our body, do not hesitate to consult the biology section.

If you want to read more articles similar to Parts of the central nervous system, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Nieuwenhuys, R. (2009). The human central nervous system (Vol. 2). Editorial Médica Panamericana SA.
- Estrada-Reyes, R., Ubaldo-Suárez, D., & Araujo-Escalona, A. g. (2012). Flavonoids and the central nervous system. Mental health, 35(5), 375-384.