Examples of PHRASES with DIRECT and INDIRECT complement
In previous lessons we have seen the different verbal complements that exist and we have studied what syntactic function each of them performs within the sentence. Well, in this article by a PROFESSOR we are going to focus on two of the most important and recurring verbal complements of all of them: direct complement (CD) and indirect complement (CI).
We will explain in detail their characteristics, functions and fundamental differences between one and the other and we will accompany the lesson with examples of phrases with direct and indirect object. Keep reading!
Index
- The direct complement (CD)
- The indirect complement (IC)
- Exercise: Phrases with direct and indirect object
- Solution of sentences with direct and indirect object
- Difference between direct and indirect object
The direct complement (CD)
The direct complement (CD) It is, without a doubt, one of the most important verbal complements since it is the one that appears most frequently in the vast majority of sentences.
The main characteristic that defines the direct object (also known as direct object) is that it is the predicative element that directly receives the action carried out by the verb. This is another reason why it is so important on a syntactic level.
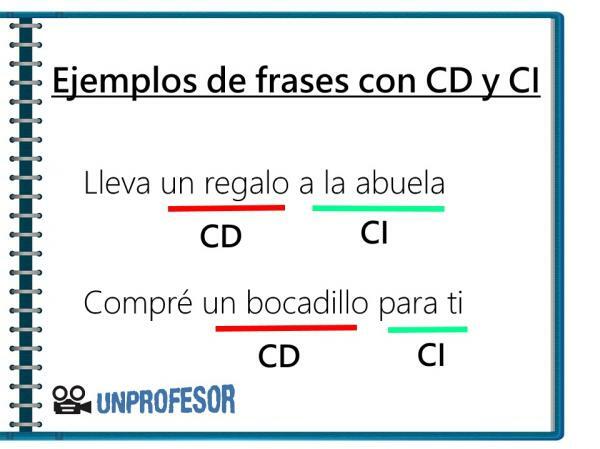
Let's see it through an example of a direct object phrase:
I want a coffee
"Un café" directly receives the verbal action implicit in the verb "want". In this sense, direct object is irreplaceable and, in the case of a transitive verb, the presence of this complement is mandatory. In other words, we can add as many complements as we want to the previous sentence, for example, "I want a coffee right now" or "I want a very hot coffee."
These circumstantial complements are not necessary and can be removed without the sentence losing its meaning. However, direct object cannot be removed since the phrase would be incomplete or it would come to mean something else entirely.
In this video of a PROFESSOR we give you tricks to identify the direct object.
The indirect complement (IC)
The indirect complement (IC) is defined as that verbal element that experiences verbal action second or indirectly; that is, in the background with respect to the direct object (CD). Therefore, hierarchically speaking, the indirect object (also called indirect object) is just behind the direct object.
Let's see one phrase with indirect object that will help us understand this concept:
Bring a coffee to your boss.
In this sentence, "un café" is the direct object (CD) that receives directly and in the first place the action of the verb "carry". "To your boss" is the indirect object (IC), which receives the action just second, after the direct object.
In order not to confuse both plugins with each other, you should keep the following in mind:
- The indirect object (CI) always has a preposition before it, usually it is usually "to" or "to". The direct object (CD) is not always preceded by a preposition, only if said complement refers to a person, in which case the preposition "a" is preceded, as in "I visited my grandmother".
- The indirect object (CI), when it is placed before the verb, is doubled by the unstressed pronoun "le", "les" ("They gave Juan a car"), while the direct object (CD) did not.
In this other video we give you more tricks to identify the indirect object.
Exercise: Phrases with direct and indirect object.
Next, as an example we show you a series of phrases with direct and indirect object so you can put yourself to the test:
- 1. I think Marta bought her mother a book for her birthday.
- 2. Pedro and I have to find a wedding gift for my older sister.
- 3. This morning a package arrived for my roommate.
- 4. Did you bring the wine I asked for my cousin?
- 5. We are going to give my grandmother a bouquet of flowers for her birthday.
- 6. My brother tells my mother about his problems every day.
- 7. I sent my best friend a postcard last week and it hasn't arrived yet.
- 8. The policeman put the handcuffs on the offender.
- 9. The teacher thanked the students for their efforts.
- 10. Adrián threw water on the plants.
Would you be able to identify the direct object (CD) and the indirect object (CI) in each of the previous sentences? Go ahead and share your results with us!
(You have the solutions in the next section)
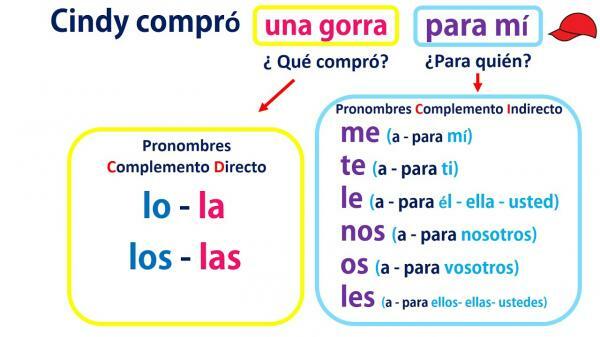
Image: Youtube
Solution of sentences with direct and indirect complement.
After completing the previous exercise, here is the solution so you can check if your answers are correct:
- 1. I think Marta has bought a book (CD)to his mother (CI) for his birthday.
- 2. Pedro and I have to find a wedding gift (CD) for my sister mayor (CI).
- 3. This morning a package arrivedfor my roommate (CI).
- 4. You've brought the wine (CD) what did i ask of you for my cousin (CI)?
- 5. We are going to give you to my grandmother (CI)a bouquet of flowers (CD) for his birthday.
- 6. My brother counts the problems of him (CD) to my mother (CI)every day.
- 7. Last week i sent you a postcard (CD) to my best friend (CI) and it hasn't arrived yet.
- 8. The policeman placed the handcuffs (CD) to the offender (CI).
- 9. The teacher thanked to the students (CI) their effort (CD).
- 10. Adrian cast water (CD) to plants (CI).
Difference between direct and indirect object.
Now that you know some direct and indirect complement phrases and you can learn to recognize these verbal complements, next we are going to make a summary about the differences between both complements and that, thus, you can learn to identify them better.
The most notable differences are as follows:
- The Direct Plugin it's related directly with the action indicated by the verb. On the other hand, the Indirect Complement is indirectly related to the verb.
- The CD can go with a preposition or not, it is optional and depends on each case. But the CI is always preceded by a preposition that will indicate that it is an Indirect.
- The pronouns that replace the CD are "lo, la, los, las". In contrast, in the case of IC, the pronouns are "le and les".
- In the case of a passive prayer, the CD becomes the Subject. But in the case of IC, when it becomes passive, it remains Indirect, that is, its function is not changed.
As you can see, there are many differences between the direct and indirect complement and they will help you to easily identify these verbal complements. In this way, you will be able to perform syntactic analysis and better understand how the language works.
If you want to read more articles similar to Phrases with direct and indirect object, we recommend that you enter our category of Grammar and Linguistics.


