Sociolect: definition and examples

Image: Slideshare
Language has a social character, that is, it is shared by a community. But it must be borne in mind that every society is divided into different social classes; each of them constitutes a group of speakers with certain linguistic features that form what we know as a sociolect or diastratic variety. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will provide a definition of sociolectas well as some examples.
While language is the human ability to communicate through the use of linguistic signs, language language it is the materialization of this capacity in a community of speech. Within each language there are also different varieties, which are determined by the geographical, social and situational circumstances of the speakers.
According to the communicative situation, we find the different varieties diaphasic, also called style varieties or log varieties. Each speaker uses some of these varieties and rejects others according to the moment.
There are also some varieties that depend on linguistic competence: on the one hand, the
dialectsgeographic or diatopic varieties are related to the place of origin or residence of the speaker; on the other, the diastratic or sociolect varieties They are related to supra-individual circumstances such as the level of education or the social class of the speaker.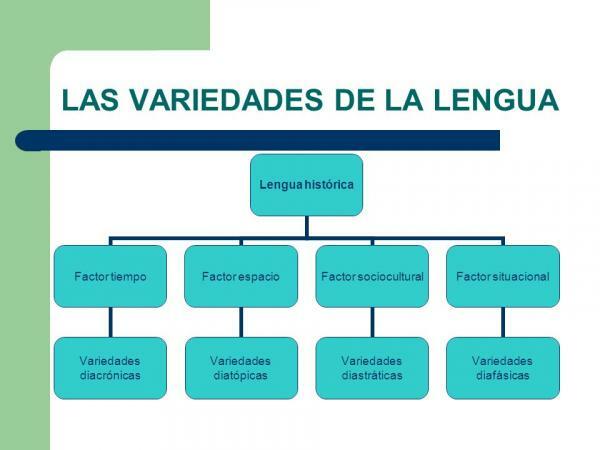
Image: Slideplayer
On this occasion we are going to focus on sociolects, those modalities of the language that they belong to a certain social stratum. The most important factor is the level of culture and education of the speakers. Sociolects change according to the following factors:
- Age: Each generational group has its own traits (young people are innovative, especially when it comes to vocabulary and expressions; while older people tend to accept changes worse).
- The habitat: An urban language (innovative and influenced by continuous linguistic fashions) and an urban language (more conservative and with a more relaxed pronunciation) can be distinguished.
- Its trades and activities: Differences especially in the lexical-semantic level.

Image: Slideshare
These factors make us distinguish the following social varieties:
1. Cult level
The cultured level is typical of educated people and with a high cultural level. It is considered an example of correction. Its main characteristics are the following:
- Correction in pronunciation, grammar, and lexicon.
- Lexical richness, which includes abstract concepts and can cover all areas of culture.
- Share characteristics of the literary tradition, and collect their wealth.
2. Standard level
The standard level constitutes a level of medium formality that meets the normative requirements of the language in a less rigid way than the educated level. It is the proper level of the media and education.
3. Popular level
The popular level is that of everyday life. It has the following characteristics:
- A subjectivity that is materialized in a frequent use of interjections, irony and exclamations.
- Linguistic economics, which causes the existence of unfinished sentences, short phrases, fillers, etc.
- Frequent listener appeals.
- Use of sayings, set phrases and proverbial language.
4. Vulgar level
The vulgar level is that of speakers with a low level of schooling. It has a poor lexicon and a simple grammar. Constantly alter the norm and introduce vulgarisms, which can be:
- Vulgarisms fonetics: accent shifts (*acrobatics), vowel indecision (*tualla), consonant simplification (*true, *ovum), consonant relaxation (*colorá, *hello), change of consonants (*cocreta).
- Lexical vulgarisms: loneliness (*explode), figurative lexicon (*snitch), etc.
- Morphological vulgarisms: analogies (*haiga); leísmo, laísmo and loísmo; dequeísmo and queísmo; verbal alterations (*did you dress).
- Syntactic vulgarisms: change of order (*I forgot), mismatches (*people are hungry), etc.

Image: Brainly
So that you better understand the difference in language levels that we have indicated in the section above, below we will leave you some example texts so that you understand each of these levels:
Example of cultured level
"Antonio Pigafetta, a Florentine navigator who accompanied Magellan on the first voyage around the world, wrote as he passed through our South America a rigorous chronicle that nevertheless seems an adventure of the imagination. He related that he had seen pigs with the navel on their backs, and some legless birds whose females hatched on the male's back, and others like tongueless gannets whose beaks looked like a spoon. He recounted that he had seen an animal spawn with the head and ears of a mule, the body of a camel, the legs of a deer, and the neighing of a horse. He said that the first native they found in Patagonia had a mirror placed in front of him, and that this fiery giant lost the use of reason due to the fear of his own image ".
Gabriel García Márquez, "The loneliness of Latin America"
Standard level example
"Almost two thirds of marine natural spaces are in international waters, beyond the immediate control of the countries. This effectively makes it a wild west marine, where the fishing fleets have open bar. There are certain laws that regulate fishing in these areas, but there is no binding agreement for conservation on the high seas, although the United Nations is negotiating such a treaty. It is crucial that it is ensured that marine nature cannot be exploited. "
Various authors, The country, "The future of 70% of the virgin spaces of the planet depends on five countries".
Example of colloquial level
- "Whoever gets close !!!
- Yes, yes, a lot of theater now -said Sebas-; then you give it to each sit-in, which wears out the living in the corners, the poor girl, waiting.
- Yes it will be infundios! That is uncertain.
- Well, let her say it herself, let's see if she doesn't.
- I throw you!!! -amagama Santos lifting in his hand a can of sardines.
- Less!
- Chss chss, let's see that for a second... Miguel cut in. That can.
- Is?
- Yes that; You will see !!!
- -There it goes".
Rafael Sánchez Ferlosio, The Jarana
Example of vulgar level
"You know what pisses me off? In other words, with the last photo I uploaded, they liked people that I passed by, who followed them and such and saw their publications and did not give them. But now I am sorry because this gave him and I do not like his photos. Did you hear it? Jobá, how disgusting you are. "