ALL parts of a NARRATION

To better understand how is the way of a narrative text all the elements that are part of this textual typology must be understood. In this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to find out what all the parts of a narrative analyzing them one by one so that you can better understand how to structure and create these texts. In addition, we will also discover the essential elements of a narrative and that contribute to characterize this type of text and differentiate it from the rest.
Index
- The approach, the first part of the narrative
- The knot, one of the essential parts of the story
- The denouement of the narrative
- Narrative elements
- Structure of the narrative
The approach, the first part of the narrative.
When we talk about the parts of a narrative, we are referring to the internal structure, that is, the way in which it is present the facts within the text and that allows the reader to engage in reading and keep an active interest in the story.
Let's remember that a
narrative text It can have real or invented elements, however, they have to be exposed following a logical order and that they give us information that was previously unknown. The participation of characters is essential in this type of text as well as the use of literary resources that manage to give a more artistic and impressive corpus to the text.But to know the parts of a narrative it is important that we start with the first of all: the approach or beginning of the narrative. It is about the presentation of the theme, the plot and the first appearance of the characters. Normally the approach takes place at the beginning of the narrative although, some authors, may Reversing the literary structure and starting with the middle or the end, however, is not the most common.
Characteristics of the narrative approach
- The argument is presented in a general way
- We know the narrative voice and we see what type of narrator is the one who tells the story
- The characters are briefly introduced to us so that we better know what they are like and some basic characteristics
- It is usually the part of the narrative that is at the beginning of everything, with which the text begins

Image: SlidePlayer
The knot, one of the essential parts of the narrative.
Continuing with the most prominent parts of a narrative, we will now talk about the knot or conflict. This is when the dramatic events or turns that endanger the situation of stability or normality with which the story began. It is the action that produces the "problem" of the argument and that has to be developed. It is essential that there is a knot in a narrative text because, otherwise, we would not speak of a narrative but we would find ourselves before another type of text such as, for example, a descriptive text.
Due to this knot, the characters will have to resolve situations of all kinds to regain the stable situation that existed at the beginning of the narrative. Normally, in narratives, the plot knot is what makes the characters undergo a series of changes and that, therefore, they live an evolution that will not be the same character who has started as the one who has finished the story.
At the moment of the knot, new characters can also appear that are the cause of this instability. In many cases a antagonist, that is, a character who is contrary to the protagonist and who is the main cause of the plot twist.
Characteristics of the narrative knot
- It is the part that generates the main action of the narrative text
- It is essential to be able to talk about a narrative
- The main characters will be influenced by this knot and, from here, will come their change or evolution within the text
- It has the climax: that is, at the knot of the story is when we find the climax of the narration, the key moment and most conflict in which the true nature of the characters

Image: Slideshare
The denouement of the narrative.
And we end with the third and last part of a narrative: the denouement. That is, it is about the final resolution of the conflict that has taken place in the knot. After having known the characters in a previous and natural way during the presentation, an event has occurred that has disrupted everything (the knot) and, when it comes to solving this conflict, it has been when the outcome has taken place, the way to solve the problem and to conclude with the story.
This narrative part also known as "conclusion" and contains the final elements of the resolution of the conflict that has arisen. In this ending, the character has had to reach (or not) his goal, the problem of the knot is over and a final situation is reached that may be better or worse than the first but which will seldom be same. The objective is that the characters, due to the raised knot, have undergone some kind of change.
Outcome characteristics
- This is the situation resulting from the knot
- The characters or the space have had to undergo some changes and, therefore, they will no longer be the same as they were at the planting or the beginning of the narrative
- It is the final part of the plot and where the story ends
- This ending can be left open and, also, it can be worse than what had been told at the beginning. All this will depend on the style and message that the author wants to give
- The characters will not be the same at the beginning as at the end of the plot. The knot will have changed them for better or for worse

Image: SlidePlayer
Elements of the narrative.
Now that we know the parts of a narrative, it is important that we stop for a moment to know the elements of the narrative that make this type of text unique and different from the the rest. The highlights that make up a narrative text are the following:
- The figure of the narrator: in a narrative there is someone who "narrates" the events that are told and this narrator may have different voices. There are different types of storytellers such as, for example, the first person, the second person or the third person also known as omniscient.
- Existence of action: We have already said it in section 2 but we repeat it again. In order to talk about a narrative text, it is essential that something happens in the story, that there is a main action that generates a change or a conflict in the characters. If this does not exist, we are not facing a narrative but rather another type of text.
- Characters: It is also essential that there are characters within a narrative since they are the main agents who star in the plot that is being told. The characters are usually differentiated between main and secondary depending on the degree of prominence they have in the story. There may also be an antagonist who would be the opposite character to the main character and who, on many occasions, is one of the agents of change.
- Narration's space and time: it is the context that sets the story. You have to define well where the plot occurs and when it is taking place. Time is also used to describe the rhythm of the exposure and it is when we find time that it can be linear (that follows the beginning-node-end structure) or non-linear (that inverts this structure with literary or dramatic motifs).
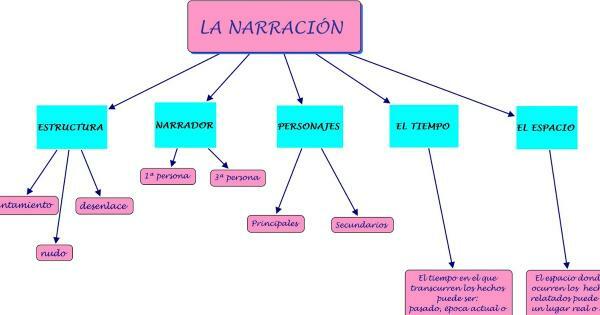
Image: Suro grade 10. group 1
Structure of the narrative.
And to finish understanding what a narrative text is like, it is important to discover the narrative structure. The author must structure the information and the argument taking into account two different models:
- External structure: it is the physical way of structuring the entire text, that is, dividing the information into chapters, volumes, episodes, and so on.
- Internal structure: is the way in which the author orders and distributes the narrative. In other words, the approach, the knot and the outcome are part of this internal structure, but also the arrangement of time, that is, how the development of the plot is presented.

Image: Partsdel.com
If you want to read more articles similar to Parts of a narrative, we recommend that you enter our category of Writing.



