DIAPHASIC variety: definition and characteristics

Depending on the communicative context in which we find ourselves, we can use one linguistic register or another. And it is not the same to be talking to your parents than to talk to your boss, right? The adaptation of the language that we carry out according to the situation in which we are is what is known as diaphase variety. In this lesson from a TEACHER we want you to know in detail the definition and characteristics of the diaphase variety, one of the varieties of the language that is the one that contains the linguistic registers such as the formal, informal and vulgar register. Here we tell you everything.
Index
- The varieties of language in sociolinguistics
- Definition of diaphase variety
- Characteristics of the diaphase variety: the registers of the language
- Slang
The varieties of the language in sociolinguistics.
At the level of sociolinguistics, the language varieties, that is to say, the different uses that we give to the language depending on the social context in which we find ourselves. This context can be geographical, sociocultural, functional or historical and, depending on it, we can end up using one linguistic variant or another. The diaphase variety is one of these 4 variants that we find in the language but before knowing it in detail, we are going to discover
what are all the varieties to better understand this concept:- Diaphase or functional variety: This variety occurs when the speaker chooses different language modalities according to the communicative situation in which he finds himself. This is where the registers of the language come from, which are divided into colloquial, formal, familiar, technolect, and so on. Here we also find the jargon that is the variety that is used in a specific professional field.
- Diastratic or sociocultural variety: is what refers to the levels of the language, that is, depending on the knowledge of a speaker, he or she can use the language in a more or less cultured way. People with a higher level are proficient at all language levels and can adapt their language to the appropriate context; people with less knowledge and education do not master the most cultured language and, therefore, their adaptation to the communicative context is lower.
- Diatopic or geographical variety: It is what refers to dialects and regional languages. This linguistic variety appears for geographical reasons since depending on the territory in which we are, the language may have different characteristics. This would be the case of the Spanish that is spoken in Andalusia, of the Spanish that is spoken in Argentina, of the Spanish that is spoken in the Canary Islands and a long etcetera.
- Diachronic or historical variety: they are the different states that the language has experienced throughout history. The change that Spanish, for example, has undergone since it became a Romance language from Latin and until it became the prestigious language that it is today.
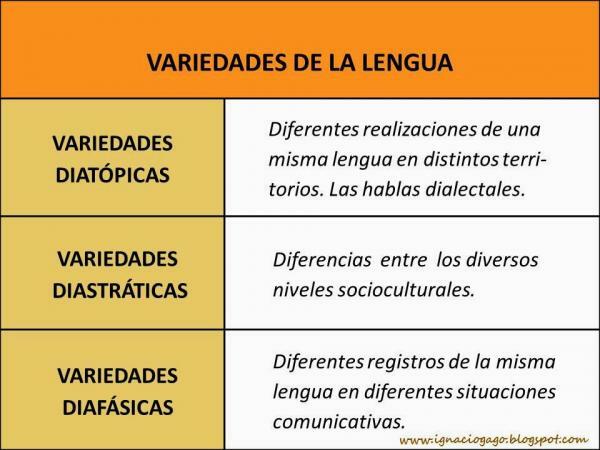
Image: Filiberto Márquez
Definition of diaphase variety.
Once introduced to the subject, now we are going to discover the definition of diaphase variety so that you understand in a concrete way what we mean when we talk about this variety. As we have already mentioned, this variety is also known as "functional" and this is because, depending on the communicative context in which we find ourselves, we can use the language in one way or another.
It is a variety that takes into account the communication status where we are: talking to your boss is not the same as talking to your partner; It is also not the same to speak to a child than to speak to a teenager. These changes that we make when speaking and using language depending on the moment in which we are is what is known as diaphase variety.
One of the most decisive points in this variety is the degree of formality that we give to our speech. With a boss we will use a more formal grade and with our friends a more informal grade. This is given by social aspects such as trust, familiarity, respect, and so on. It is the speakers who choose which will be the most appropriate register of the language according to the communicative situation in which they find themselves.
In this sense, linguistics differentiate different registers of the language that have to do with the diaphase variety. Although there is not yet a common agreement on how many records there are, in a generic way these are differentiated:
- Cult or formal
- Colloquial
- Vulgar
- Jargon

Image: Slideshare
Characteristics of the diaphase variety: the registers of the language.
The language registers they always depend on the communicative context in which we find ourselves. We will use an informal register when we are talking to our parents and a more educated one when we are doing an oral presentation, for example. Therefore, depending on the situation in which we find ourselves, we will choose to use one registry or another.
In general terms, linguists determine the existence of these language registers:
- Formal registration: is the one used when we are within a more serious and sober context. This register is the one that can be used by people with more education and with a greater knowledge of the language because it requires a certain knowledge of the language and its rules. This registry is often used between people who do not know each other well or between more professional or academic contexts. It is characterized by the use of a high vocabulary, the absence of vulgarisms and both grammatical and spelling errors are avoided. This record may include the use of technicalities of the language.
- Colloquial or informal: let's not confuse the colloquial register with the vulgar one because it is not the same. The colloquial is that register that is used in familiar and trustworthy environments, in more relaxed environments and where there is some relationship between the speakers. This register is used by all speakers when we are in a more relaxed environment.
- Vulgar registration: This register is associated with the sociocultural level of the speaker and, in general terms, it is the register used by people with less knowledge of the language. This causes an incorrect use of the language due to the lack of knowledge in this regard. Some of the errors that this registry entails are phonic errors, constant use of fillers, use of generic words due to lack of lexicon, etc.

Image: Pinterest
Jargon.
When we talk about slangWe are referring to a type of language that is used in very specific communicative contexts. And it is that depending on the social group in which we are, we can find that a jargon is used determined and that, above all, has its own lexicon and that is only understood within the group Social.
There are different types of jargon such as the following:
- Social jargons: are those used by different groups in society and that serve to identify and differentiate themselves from the rest. A clear example is the jargon spoken by rappers, by young people, by car lovers, and so on.
- Professionals: these are the words that are used within a specific professional field such as, for example, medical jargon, lawyers, programmers, etc.
- Tech jargon: are the new words that have appeared within the technological field and that are only understood if they are used in a communicative context that talks about technological issues.
Within the jargons, we also meet slang which is a type of jargon typical of marginal groups. A clear example would be the slang that is spoken in prisons, that is spoken among the world of drugs, etc.

Image: Slideplayer
If you want to read more articles similar to Diaphase variety: definition and characteristics, we recommend that you enter our category of Grammar and Linguistics.
Bibliography
- Briz, A. (2010). The colloquial and the formal, the axis of linguistic variety. Recovered from: http://ifc. dpz. es / resources / publications / 29/95 / 11briz. pdf [Accessed April 3, 2014].
- Prados-Lacalle, M. (2014). The treatment of the varieties of Spanish in the materials for the teaching of Spanish as a foreign language.
- LASSO-VON LANG, N. I. L. S. TO. (2005). Linguistic varieties and languages in contact in the Spanish-speaking world. AuthorHouse.