DIATOPIC variety: definition and characteristics

A language, due to the use, the particularities of its speakers, the area in which it is spoken and the contacts it has had with other types of languages, presents a series of dialect variations. In this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to focus on one of these variations, the diatopic variety through your definition and characteristics. Through this explanation you will be able to verify that the language is a variable and that it presents different modes and dialects depending on where we are.
Index
- What is diatopic variety: easy definition
- Characteristics of the diatopic variety
- Northern dialects of Spanish
- Southern dialects of Spanish
What is diatopic variety: easy definition.
The diatopic variety of the tongue is also known as geographic or dialect. This means that the language will be different depending on where the speaker lives or grew up. The Spanish it is not the same in all geographic areas where it is spoken.
You will have noticed a great diatopic variety in the Spanish that is spoken in America, but also in that spoken in the Iberian Peninsula itself. Each of them has its own characteristics or traits that make it appear as a
dialect.At this point, it is essential to know what a dialect, because the diatopic variety is nothing more than the different dialects that we can find within the same language according to a geographical criterion. Thus, we can point out that dialects are systems that have signs, expressions and variations corresponding to a specific geographical area and that they are part of a common language.
Spain has different regions and the dialects of each of them are different, these make up the diatopic variety of our country and we can divide them into the following:
- Northern dialects
- Southern dialects

Image: Slideshare
Characteristics of the diatopic variety.
Now that you know the definition of diatopic variety, it is important that you know what its main characteristics are so that you can easily recognize it:
- They are recognized within the same language: Because they derive from a common language, they are understood by the speakers of that language.
- They present different records: Depending on the way they are used, they will present different registers, that is, they also have different levels, whether they are colloquial, formal or informal.
- They are local: these varieties are located in a specific place. That is, there is a group of speakers defined by geographical area. Although the rest of the speakers of the language from which it comes can understand it, they belong to a certain place.
- Common writing: they maintain writing and literary tradition with the language of origin.
- They are historical: geographical variations serve historical reasons, either due to contact with other languages or due to different own elaborations referring to different factors.

Image: Slideshare
Northern dialects of Spanish.
The dialects in Spainthey are differentiated by northern and southern. The northern ones are those variations of Spanish that are spoken in the northern half of Spain. Due to the geographical area that occupies its clearest influence is that of Castilian, although between them they represent different variations of their own. It could be said that the northern dialects are those that extend through the provinces of Ávila, Salamanca, Guadalajara, North Albacete and Cuenca.
Northern Castilian dialect
It is used in the northern half of Spain and is a variation of Spanish. It has some features of its own such as:
- The ch it is pronounced in a very strong and marked way.
- Diphthongs and hiatuses are usually elided when speaking.
- The sounds ll and Y they have different pronunciation.
- Sound replacement d when it goes to the end of a word by the sound z.
- Use of laísmo and leísmo: change of possessive pronouns. In some areas of Castilla y León one can also speak of Loísmo.
- Letter introduction r in the imperatives, that is to say, substitution of callaos by callaros.
- Preposition of the article the to the particle what.
Aragonese dialect
It is used in the autonomous community of Aragon and is influenced by Spanish and Catalan. Among its particularities are:
- In the Ebro valley areas, the end of sentences ending in vowels are pronounced with more intensity.
- Word accentuation: there is a tendency to flat or acute accentuation, regardless of the esdrújulas that become flat.
- Hiatuses tend to disappear
- Use of the diminutive –ico or –ica.
Riojan dialect:
It is used in the La Rioja area and due to its proximity to Aragon and the Basque Country, it has many influences from the Aragonese and Basque dialects. Its characteristics include the following:
- The ll on many occasions it is replaced by groups of letters that have already disappeared, a very clear example of this is the use of flame instead of flame.
- Replacement of the imperfect past of the subjunctive by the conditional.
- Use of compound tenses versus simple ones.
- Replacing the h initial by F in the beginning of some words
- The prefix loses the initial d to become es-
Leonese dialect
It is spoken in Castilla y León in the provinces of León, Zamora, Salamanca, Palencia and Valladolid. Its characteristics include the following:
- The j is pronounced loudly
- The s has a weak pronunciation
- The x it is not pronounced and is replaced by the sound s.
- Use of diminutives like -in, -ino, -ina.
- Use of archaisms
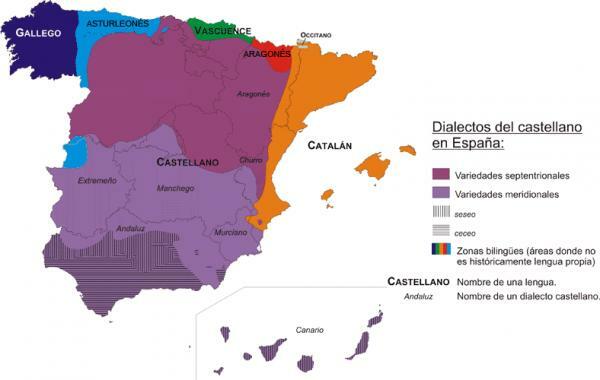
Image: Esacademic
Southern dialects of Spanish.
Southern dialects are those that are used in the southern half of the peninsula. For historical reasons, these territories acquired Castilian as a language from the 16th century onwards, hence there are variations with respect to it. Within the southern dialects we find:
Andalusian dialect
Andalusian is a dialect of Spanish with arabic influences. It is spoken in the southern part of the Iberian Peninsula in Andalusia and in the autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla. Due to this influence with Arabic they have a series of own characteristics such as:
- The seseo: is pronounced s instead of z or c.
- The lisp: pronunciation of the z instead of the s.
- Yeísmo: disappears ll and is replaced by the Y.
- The ch is pronounced in a more relaxed way assimilating to sh.
- Use of the pronoun you instead of you to refer to the second person plural.
Extremadura dialect
In this dialect, due to the fact that the area was inhabited for a long time by emigrants from the kingdoms of Castilla y León during the reconquest, some of their own traits are preserved. On the other hand, they also have the influence of the Andalusian dialect due to their proximity. Its features include:
- The d final in syllables becomes l or r
- The l it is changed by the r in those words that have cl, fl or pl at the beginning of them.
- Yeísmo: there is no distinction between ll and Y, both are always pronounced with the second.
- The d when it is placed between vowels at the end of words.
- The h words are aspirated, transforming into a sound close to that of the j.
Murcian dialect
This dialect has had influences from different dialects such as Castilian, Aragonese and Catalan from the north of the peninsula. On the other hand, it also receives influences from the Arabs as it is close to Andalusia. It occurs in the areas of the Southeast of Albacete, the South of Alicante, Murcia, Northeast of Granada and Jaén and Almería. Among its characteristics we can point out the following:
The consonants are pronounced in a relaxed way and sometimes disappear when they are between vowels.
- When the s is at the end of a syllable is aspirated.
- Seseo that consists of the substitution of the c and the z by the sound s.
- Yeísmo: there is no distinction in pronunciation between ll and Y.
- Use of the diminutive suffix -ico: this is directly influenced by the Aragonese dialect.
Manchego dialect:
- It is the dialect used in some areas of the autonomous community of Castilla La Mancha. Manchego is spoken in Ciudad Real, Albacete and in the south of Toledo and Cuenca. Its features include:
- Use of archaism: words used in the past and that are already in disuse in other areas of the country.
- Using words from the Aragonese dialect of this also preserves a very similar intonation.
- Use of the masculine to refer to feminine names and vice versa: words such as sheep, rano or serpent are used.
Canarian dialect
It has influences from Castilian and Andalusian. It is spoken in the Canary Islands and has a series of differentiating features:
- Use of l instead of final r.
- Aspiration of the s at the end of the syllable.
- Yeísmo: replacement of the ll for Y in all cases.
- Use of the seseo: z and the c becomes s sound.
- Use of you: it is used to replace you in the second person plural.
- The ch is pronounced similar to Y.
Madrid dialect
It is a dialect spoken in the city of Madrid and in those geographical areas that are around it. It has some own linguistic variations such as:
- The d at the end of the words by the z.
- Disappears d when it goes between vowels in the participle of any verb.
- Yeísmo: there is no distinction in pronunciation between the sound ll And the sound Y. Both are pronounced as one Y.
As you see in the Spanish language there are many variations. If you want to find more lessons like diatopic variety definition and characteristics, follow our sections where you will find information on other topics.
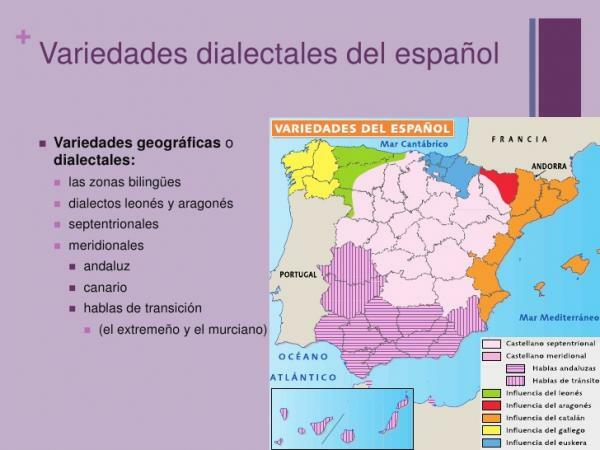
Image: Practice your language
If you want to read more articles similar to Diatopic variety: definition and characteristics, we recommend that you enter our category of Grammar and Linguistics.