PLANCK'S CONSTANT: simple definition
The Planck's constant is one of the fundamental physical constants best known and most important in science. Along with other constants such as the speed of light, this constant is able to accurately describe properties of matter that we cannot even see.
The simple definition of Planck's constant is "constant in quantum physics that allows us to determine the amount of energy corresponding to a quantum or photon." In other words, Planck's constant is a number that relates, using the Planck's constant formula, the energy of a photon with the frequency of the wave. If you want to know more about the Planck's constant, simple definition and how important it is in science today, keep reading this lesson from a TEACHER!
Planck's constant and Planck's constant formula.
To understand the discovery and significance of Planck's constant we have to remember one of the fundamental theories of chemistry: the Quantum theory. In quantum theory, energy is made up of particles, since it is a type of matter. Light - and any other electromagnetic radiation - is made up of particles called
photons.At the time, researchers of the time believed that energy exchanges between matter and radiation was carried out continuously, but when it was proposed to study it, the experiments proved the contrary. The interaction between matter and radiation it always produced a discrete energy exchange, that is, it had values determined or proportional to these and could not take any value.
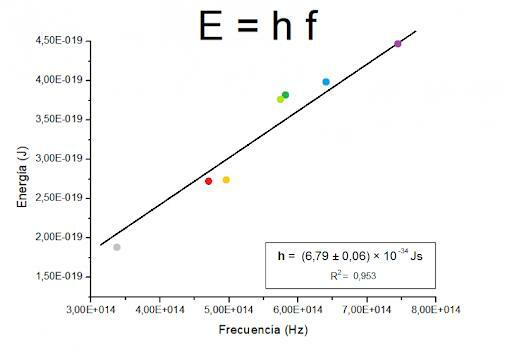
In 1900, Planck and his colleague Rubens began to study the radiations absorbed and emitted by a black body and on December 14, for the first time, at the German Physics Society, Planck put forward the hypothesis that led him to this law: the quantification of energy. Planck explained then that the radiation emitted by a black body behaves as if it were made up of "packets" of energy. The value of each of these packets would be ε = hν, where "v" is the frequency of the radiation and "h" is the constant known today as Planck's constant (h = 6.63. 10 -34 joules per second).

Image: Tes
Importance of Planck's constant.
Planck's discovery may seem unimportant today, but it is not. On 1918, the German physicist received the Nobel Prize for his "breakthrough discoveries that paved the way for quantum mechanics."
Using the hypothesis proposed by Planck, which would later become theory, the researchers showed that the radiation was made up of energy packets. This would later lead to the discovery that electromagnetic radiation is waves but is made up of particles, photons. Today this theory is known as the wave-corpuscle duality phenomenon. Planck's discovery was key to many discoveries by other great scientists of the modern era:
- The photoelectric effect. Einstein, analogously to Planck, proposed that the absorption of light by a metal occurred in a discrete way, to quanta, and its corresponding emission of electrons, was also in packets. This today is known as the Photoelectric Effect and, again, Planck's constant was the protagonist for its discovery.
- Bohr's atomic model. Another discovery, no less important, was made at the beginning of the 20th century with the Bohr Atom model and its postulates. This model revolutionized the concept of the atom and for its postulation and demonstration it intervened again the concept of the emission and absorption of light by matter in a discrete way demonstrated by Planck.
- Heisenberg's indeterminacy principle. The indeterminacy principle, postulated by Heisenberg, proposes that it is impossible to measure simultaneously, and with absolute precision, the position value and the amount of movement of the a particle. To demonstrate this, the German researcher relied on Planck's constant formula.
Planck's constant relates the energy of a particle to its wavelength and, therefore, constitutes the fundamental magnitude of mechanics quantum that was not only used to make later discoveries, but is widely used today in the practice of many Sciences. At present, this constant is widely used in physical to measure the energy of a radiation, not only in a unit of energy, but also in units of length and frequency. Planck's constant is also used in the field of astronomy since, by using the black body law, the temperature of an object whose emission is centered at a certain frequency can be determined.
Image: Slideplayer
If you want to read more articles similar to Planck's constant: simple definition, we recommend that you enter our category of Modern physics.
Bibliography
- Artuso, C., & Satz, A. (2001). Determination of Planck's constant using LEDs. Laboratory, 5.
- Samaniego, W. P. Á., Samaniego, B. Á., & Álvarez, D. M. (2013). A physical interpretation of Planck's constant. Central Chemistry, 3 (2), 3-10.
- by Amorim, M. R & Sá Ferreira André, P. S. B. TO. Cordobés, J.M (August 8, 2014). Fundamentals in the Classroom: measuring Planck's constant. Recovered from https://www.scienceinschool.org/es/2014/issue28/planck
- Sancler, V. (s.f) Planck's constant. Recovered from https://www.euston96.com/constante-de-planck/