What was the last ice age on our planet

Image: ABC.es
In previous lessons from a TEACHER we have discussed the main glaciations, briefly explaining some of them, but without focusing specifically on any of them. It is important to know these glaciations and especially those that have taken place in the Quaternary stage, that is to say, in which we are currently. Therefore in this lesson we are going to talk about what was the last ice age on our planet and that, thus, you know better the history of the Earth.
The quaternary glaciation is a stage of our planet in which there are a series of glaciations separated by interglacial periods, and that took place during the Quaternary Period, in the Cenozoic Era. The Quaternary began 2.58 million years and it continues to this day, finding ourselves in one of the interglacial periods.
The Quaternary has had 4 glaciations and 4 interglacial periods, which are the following:
- Günz glaciation: The first of the Quaternary ice ages. It started 850,000 years ago and ended 600,000 years ago.
- Günz-Mindel Interglacial: An interglacial period located between the Günz and Mindel glaciations.
- Mindel glaciation: The second of the Quaternary ice ages. It began 580,000 years ago and ended 390,000 years ago.
- Interglacial Mindel-Riss: An interglacial period located between the Mindel and Riss glaciations.
- Riss glaciation: The third glaciation of the Quaternary. It began 200,000 years ago and ended 140,000 years ago.
- Interglacial Riss-Würm: It is an interglacier located between the Riss and Würm glaciations.
- Würm glaciation: It is the fourth and last of the Quaternary ice ages. It started 110,000 years ago and ended 10,000 years ago.
- Holocene: Also known as the postglacial period, it is the interglacial period in which we are currently.

Image: Slideplayer
Once we have seen all the periods of the Quaternary we can now answer the question about which was the last ice age on our planet, making it clear that the last has been the Würm glaciation.
The Würm Ice Age is the last of the four ice ages of the Quaternary period, starting 110,000 years ago. This glaciation receives numerous names depending on the area in which the subject is treated, such as example the name of Wisconsin that receives in North America or the name of Merida that they use in Venezuela.
During the Würm Ice Age, the Homo sapiens it expanded to all continents, leaving the African continent. According to experts, humans took advantage of the frosts to be able to cross the Bering Strait, passing from Asia to America. The situation of the Bering Strait during this time is known as the Beringia Bridge, being a land bridge that united Siberia with Alaska. We could say that it is thanks to this glaciation that the human being was able to occupy all the continents, leaving Africa and occupying the entire planet.
The glaciation had numerous consequences on the planet, among which we can find the following:
- The planet's climate became much more cold.
- The glaciers reached as far as tropics.
- The continents turned ice.
- I know they froze the freshwater areas of the planet, that is, rivers and lakes.
- The shallow seas, becoming large glaciers.
- Certain areas were linked together. For example, Japan and Korea or the Philippines and Indonesia.
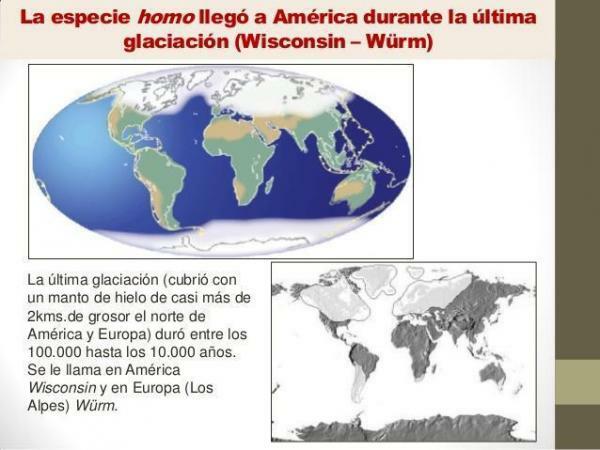
Image: Geology
It is difficult to speak in general about the Würm glaciation, since its importance and evolution were very different in different areas of the planet. The glaciation was especially concentrated in the regions of North America, Europe and Asia. Some of the areas that became ice-covered were Canada, the northern United States, the United Kingdom, much of Europe, and northern Asia.
In the Iberian Peninsula the glaciation had very relevant consequences. The Peninsula underwent numerous constant changes, turning the territory into a place with many ecosystems. This great variety of ecosystems benefits the large mammals of the area, increasing their number in these years.
In some countries the Würm glaciation is divided into three or four different periods, each country having a different subdivision. In Germany the period is divided into three, which are Würm I, Würm II and Würm III. On the other hand, in Spain it is divided into four periods and two blocks, the first block being called Old würm, formed by Würm I and Würm II, and the second block called Recent Würm, formed by Würm III and Würm IV.
