GREEK mythology: summary and characteristics

Out of all mythologies that have shaped the history of humanity, possibly the best known and most interesting is the Greek, being the one that has had the most relevance for the Western world. Its relevance stems from its great breadth, and for this reason and to know in depth its elements in this lesson from a PROFESSOR we offer you a summary of Greek mythology and characteristics.
We know as Greek mythology the set of Myths and legends that make up the culture of the Ancient Greece. They were stories transmitted orally at first, but with the passage of time they were collected in texts by important authors such as Homer or Hesiod.
The origin of Greek mythology is a mystery, but according to the latest studies the most accepted theories speak of a fusion between legends of the original peoples of the Balkans and other arrivals from the north.
Stages of Greek mythology
A key element to understanding Greek beliefs is understanding the division of stages in myths, since each of these is characterized by different elements:
- The first stage is the age of the gods characterized by the origin of the world and the birth of the gods
- The second stage is that of the gods and men and tells the stories between gods and men
- The last one is the age of heroes that tells the adventures of the great Greek heroes.
To understand any mythology it is essential to list its characteristics, being basic to understand the beliefs and myths and differentiate them from other mythologies. The main elements that define Greek myths are the following:
- They were polytheists, that is to say that they had a pantheon with many gods.
- Mythology consists of Myths and legends in which stories are told to explain the world or adventures of gods and heroes.
- They seek to explain all the events of the world through a story, everything must be explained through mythology.
- Natural events are a consequence of anger of the gods, considering that earthquakes or floods were the punishment of the deities.
- There is a kind of hierarchy between the gods, with a great differentiation between the so-called Olympian Gods and the rest.
- There were places inhabited by gods like the Olympus or the Underworld.
- The gods were responsible for the creation of the world.
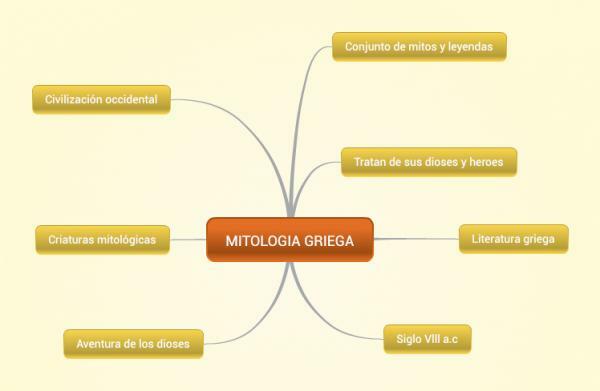
Image: Google Sites
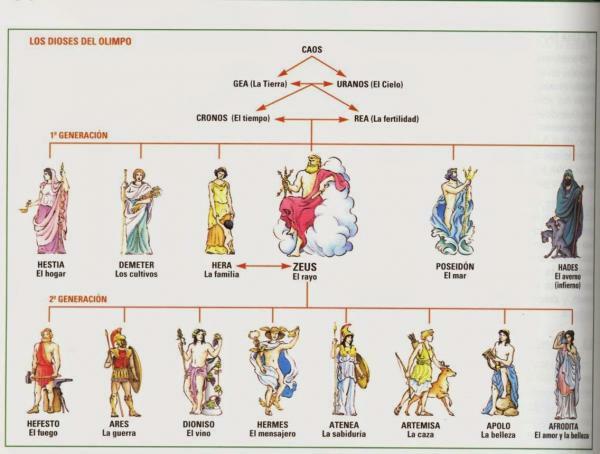
One of the most important factors in Greek mythology is the gods and, therefore, it is very important to list the different gods that make up the Greek pantheon, being essential to know their myths and legends. The main Greek gods are the following:
- Zeus: King of the gods and god of the sky and thunder.
- Hera: Queen of the gods and goddess of marriage and family.
- Poseidon: God of the seas, oceans, earthquakes and horses.
- Apollo: God of music, fine arts, the sun, medicine, beauty, knowledge, poetry and protector of prophecies.
- Athena: Goddess of wisdom, artisans and war seen from the point of strategy.
- Aphrodite: Greek goddess of beauty, sexuality, love and carnal desire.
- Ares: God of war, blood, masculinity and strength.
- Dionisio: God of the Greek mythology of wine, parties and other types of substances.
- Hermes: Messenger of the gods and god of messengers, thieves, commerce and travelers.
- Sagebrush: Goddess of hunting, the moon, archery and animals.
- Hephaestus: God of fire, blacksmiths and craftsman of the gods.
- Demeter: Goddess of nature, crops, the seasons of the year and fertility.
- Hades: Greek god of the dead and lord of the Underworld.
- Hestia: Goddess of home and family.
To finish this summary of Greek mythology we must talk about the main myths that make up the classical beliefs, summarizing roughly those that have had the most relevance of one or Another way.
Origin of the world
The origin of the Greek world tells that at first there was only Chaos, a force primal body without a body, from him were born the land called Gaea, the underworld called Tartarus and the love that it was Eros. After these births, Chaos had two other children, Erebus being like darkness and Nyx like night, who in turn had Ether and Hemera as children, who formed light. After this, the birth of Uranus took place, which together with Gea formed men creating the world.
Prometheus and fire
Prometheus he was one of the Titans who were defeated by Zeus and the rest of the gods, but he was one of the few who did not receive a punishment at first. Prometheus considered that men deserved to evolve, and so he stole the fire from Mount Olympus to teach its use to the men, being punished for it he was tied to a rock in which a bird would eat his entrails for the rest of the eternity.
The 12 labors of Heracles
Due to different circumstances by which Heracles murdered his wife and his children the Oracle of Delphi He told her that to heal his faults he had to fulfill a series of jobs that will allow him to clean his sins. The 12 works of Heracles, most of which consist of defeating powerful creatures from mythology, caused the Greek demigod to enlarge the legend of him.
The Trojan War
The trojan war it was a confrontation halfway between legend and reality in which a coalition of Greek cops met faced the great city of Troy because the Trojan prince had kidnapped the wife of the king of Sparta. Both in its causes and in its development, numerous gods appear in one of the most repeated Greek stories.
The arrival to the power of the gods
For a time Olympus was ruled by the Titans, who were descendants of the primeval forces of the world, their leader being Cronos. It is said that fearing that his sons would take away his power, the titan devoured them all, but his son Zeus was saved and later overthrew his father, this being the reason why the gods seized the power of the Olympus.
Theseus and the Minotaur
It is said that every year Athens had to deliver a series of tributes to Crete to be devoured by the Minotaur, but the son of the Athenian king Theseus volunteered to enter the labyrinth. Thanks to his intellect the king was able to kill the Minotaur, saving dozens of lives thanks to his action.




