Subatomic particles: DEFINITION and CHARACTERISTICS
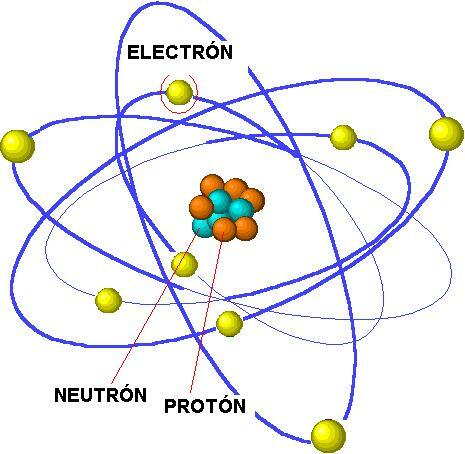
Image: The Knowledge Library
Atoms form the basic structural unit of our world. All matter is made of atoms and therefore it is essential that we know, even roughly, its structure. The atom is made up of three particles: electron, proton, and neutron, and we now know that these particles are in turn made up of others, even smaller. Although they are all called subatomic particles, in this lesson from a PROFESSOR we will study electrons, protons, and neutrons and the characteristics that differentiate them. If you want to know the definition and characteristics of subatomic particles, Keep reading this lesson from a TEACHER!
Classically, since the first atomic models were made, it has been described that these atomsmade up of three particles: protons, electrons and neutrons. Thanks to later investigations of atomic physics, it was discovered that in addition to these there were other particles that make up atoms. Currently it is known of the existence of the following subatomic particles:
- Boson
- Positron
- Electron
- Proton
- Fermion
- Neutrino
- Hadron
- Neutron
- Lepton
- Quark
- meson
This does not mean that these are the only subatomic particles that make up the atom since, due to their poor stability, size, etc. These particles are very difficult to study and therefore to discover. In the coming years, other particles can be added to this list and undoubtedly the knowledge we currently have about them will be improved.
Since little is known about the new subatomic particles, in the next sections we will only study the characteristics of the classical subatomic particles: proton, electron and neutron.

Image: SlidePlayer
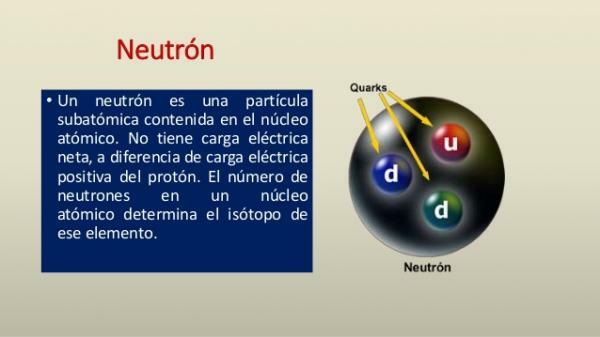
The neutron is a particle that, like the proton, is found in the nucleus of atoms. The main characteristics of the neutron are:
- The neutron, living up to its name, has neutral electric charge (0 C)
- The neutron is found in the core of all atoms except protium (atom composed only of one proton and one electron). The set of protons and neutrons, which form the nucleus of atoms, is called nucleons.
- Unlike the proton, the neutron is a particle very unstable, with a half-life of about 14.7 minutes (879.4 ± 0.6 s).
- The neutron has a proton-like mass y is 1.67492729 × 10−27 kg. Together with the proton they form a nucleus that, compared to the electrons that orbit around it, is very heavy.
- Neutrons, like protons, are made up of three quarks, so they are included within the baryons.
- Neutrons also have a 1/2 ħ spin, so they are considered fermions (half-integer spin particles).
Electrons, which can be represented as e-, are particles that can be found in free form or as part of an atom, orbiting around the nucleus formed by neutrons and protons. The main characteristics of electrons are:
- The electron has a charge equal to that of protons but with the opposite sign, that is, −1.6 × 10−19 C.
- The electron is found in the crust of the atom, rotating or orbiting around the nucleus but it can also be isolated.
- The electron is a stable particle with a half-life of about 4.6 × 1026 years.
- This particle is very small Compared to the previous ones, it has a mass of 9.10938291 × 10−31 kg, which makes it about 1836 times less heavy than the proton.
- Unlike the previous ones, the electron is a elemental particle since to date it has not been shown that it is made up of smaller ones. In fact, the electron belongs to the group of leptons, which are believed to be the true elementary particles.
- Electrons have a spin of ± 1/2 ħ, so also are considered fermions (semi-integer spin particles).

Image: SlideShare
If you want to read more articles similar to Subatomic particles: definition and characteristics, we recommend that you enter our category of The atom.

