TYPES of ATOMS: Natural, Synthetic and Others

Image: Slideshare
The term atom comes from the Greek ἄτομον ("Atom") and refers to the smallest constituent unit of matter. All matter, whether natural or artificial, solid or liquid, is made up of atoms. But if all matter is made up of atoms, how can it be so varied? The answer is easy: there are different types of atoms, which are grouped in more or less large groups to form the different matter. Thus, for example, two atoms of hydrogen and one of oxygen combine to form water while To form table sugar, 12 carbon atoms, 22 hydrogen atoms, and 11 oxygen atoms are combined. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will review what are the types of atoms that can form matter.
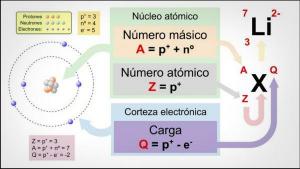
The atom is the smallest constituent unit of matter and it is formed in turn by three types of particles (neutrons, protons and electrons), which are arranged forming a nucleus of neutrons and protons surrounded by electrons. The number of protons an atom has defines the type of atom to which we meet. For example, all atoms that have a proton in their nucleus are called a "hydrogen atom." Instead, all atoms with 29 protons in their nucleus are called a "copper atom."
Therefore, we can say that there are different types of atoms, as many as atoms with different numbers of protons in their nucleus. In the periodic table we can see the 118 different types of atoms discovered so far, from hydrogen to oganeson.
Not all chemical elements are found in a normal way in nature, some of them have been generated in the laboratory, artificially. Do you want to know which ones? Keep reading!

Image: Google Sites
The natural atoms They are the atoms of those elements that are found normally in nature. So far, researchers have discovered a total of 98 natural chemical elements. Of these 98, only 88 appear naturally in appreciable quantities since the other 10 elements are produced, of naturally, in less quantity since most are products of the radioactive decay of elements more heavy. This disintegration is natural, so these 10 elements, although to a lesser extent than the other 88, also appear in nature. The 10 least common natural elements are: technetium (Z 43), promecium (Z 61), astatine (Z 85), francium (Z 87), neptunium (Z 93), plutonium (Z 94), americium (Z 95), curium (Z 96), berkelium (Z 97) and californium (Z 98).
Although more common, not all of these 88 items are found in the same way. A few of these elements, such as noble gases, gold, silver, or copper, are found in their pure form (native form). Other elements, such as alkali metals (group 1, except hydrogen) or alkaline earths (group 2), they are only found combined, in different proportions, with atoms of other elements forming compounds chemicals.
As more studies have been carried out, some elements that were believed not to exist naturally have been discovered that, although in very small quantities, they do. Therefore, if you find that different sources name a chemical element as synthetic or natural, it is not that it is not clear, but that it has been discovered later.
The artificial atoms or synthetic elements They are the atoms of those elements that are not found naturally on Earth, although it is not ruled out that at some point in the past they did. Until now, artificial atoms are 20 and in the periodic table they go from einsteinium (Z 99) to oganeson (Z 118). These elements are created by complex processes (such as nuclear fusion or mass neutron absorption) and equipment (nuclear reactors or particle accelerators). As you can imagine, the production of these elements is very expensive so they are elements that are produced in mass or in large quantities.
Synthetic elements are usually quite unstable radioactive elements, with half-lives ranging from 15.6 million years to a few milliseconds. So much so, that in some cases its existence is known but not its properties, which are deduced from similar elements and are "theoretical properties". Thus, for example, tenese has an atomic number of 117 and a half-life of its more stable isotope is approximately 78 milliseconds. Its disintegration is so rapid that it is normal that it cannot be studied in detail, although it is believed that properties such as melting point, boiling point and ionization energy can follow the trend observed in the period at which they belong. In fact, the researchers are not even sure about your physical condition, although they do predict that the tenese is solid.
The synthetic elements discovered so far are:
- Einsteinium (Es): Atomic number 99
- Fermium (Fm): Atomic number 100
- Mendelevium (Md): Atomic number 101
- Nobelium (No): Atomic number 102
- Lawrencio (Lr): Atomic number 103
- Rutherfordium (Rf): Atomic number 104
- Dubnium (Db): Atomic number 105
- Seaborgium (Sg): Atomic number 106
- Bohrio (Bh): Atomic number 107
- Hassio (Hs): Atomic number 108
- Meitnerium (Mt): Atomic number 109
- Darmstadtium (Ds): Atomic number 110
- Roentgenium (Rg): Atomic number 111
- Copernicium (Cn): Atomic number 112
- Nihonium (Nh): Atomic number 113
- Flerovio (Fl): Atomic number 114
- Moscovio (Mc): Atomic number 115
- Livermorio (Lv): Atomic number 116
- Tenese (Ts): Atomic number 117
- Oganeson (Og): Atomic number 118
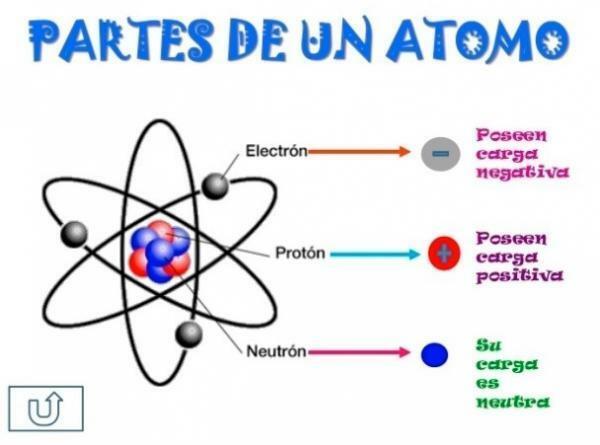
Image: Brainly