ALL properties of the ATOM

Image: SlideShare
Although we are not able to see them with the naked eye, atoms are part of all matter of our planet. All matter is made of atoms, which group together to form chemical elements, molecules, compounds, etc. The atom is defined as the smallest basic unit of matter that has the properties of a chemical element. Each chemical element is defined by the type of atom it is made of, so the final question is: what properties does the atom have? In this lesson from a TEACHER we will review the properties of the atom that make each atom a characteristic chemical element.
Index
- What is the atom?
- Atomic number, mass number, and isotopes
- Density, another of the properties of the atom
- Ionic radius and Vanderwalls radius
- Ionization energy
What is the atom?
Before entering to analyze the properties of the atom it is important that we know better what it is about. The atom is a unit formed by three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. These are organized in nucleus and cortex.
- The core It is made up protons Y neutrons, which is in the center of the atom, and is responsible for most of the weight of the atom; protons are positively charged, while neutrons are neutral so the nucleus is positively charged.
- The Cortex It is formed by electrons, which are small, negatively charged particles that rotate around the nucleus forming orbits (like that of the planets) but without ever falling to the nucleus of the atom. The cortex of the atom is in charge of interacting with the cortex of the other atoms since it is located on the outside of the atoms.
The different atoms are made up of protons, neutrons and electrons, the same in all chemical elements. So what makes there different chemical elements? The number of protons, neutrons, and electrons of which the atoms of each element are composed is different and this in turn makes each element have different features or others.

Image: SlideShare
The atomic number, the mass number, and the isotopes.
The first three characteristics have to do directly with the number of particles that make up the atom of each element.
The atomic number (Z) indicates the number of protons that make up the nucleus of an atom. So, for example, all iron atoms will have 26 protons in their nucleus. In addition, if they do not tell us otherwise, the chemical elements are in a neutral state, that is, the positive (protons) and negative (electrons) charge is the same, so they will all also have 26 electrons.
The mass number or atomic weight (A) indicates the total number of protons and neutrons that make up the nucleus of an atom. As we have already indicated before, the weight of electrons is practically negligible compared to that of electrons. protons and neutrons, so the mass number indirectly indicates the weight of the atom in question. Continuing with the example of iron, if you consult the periodic table of the elements you will see that the weight atomic of this element is 55.85, which means that all the atoms of that element will have that weight.
Finally, the isotopes of a chemical element are variants of the same atom (that is, they have the same atomic number) but a different mass number, that is, a different number of neutrons. Most chemical elements have more than one natural isotope, the element with the highest amount of stable isotopes being Tin (Sn), which has 10 different natural isotopes.
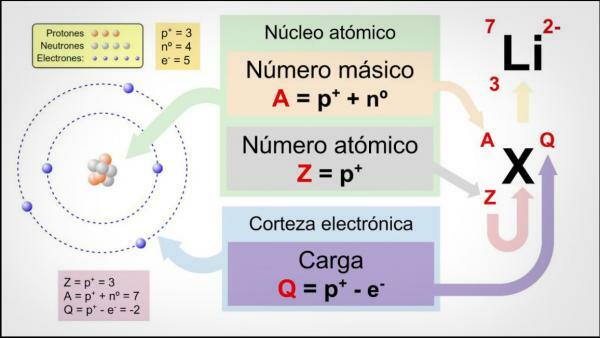
Image: ConceptDefinition.de
Density, another of the properties of the atom.
The density of an atom is the number of mass units (u.m.a) of the element that are present in a certain volume of space. The density of any substance is symbolized through the Greek letter "Ro" (written r) and its units according to the international system of units (SI) are kilograms per cubic meter (kg / m3). In the case of chemical elements, being so small, the gram per cubic centimeter (g / cm3).
In order to calculate the density of an atom (atomic density), we would have to take into account the mass of the atom and its volume. While most of the mass of the atom is in the nucleus of the same, the volume has to do with how big the atom is, and therefore the number of electronic orbitals will play a role important. Taking into account these properties and their tendency in the periodic system, we can observe that the density increases as we increase in a group and also increases as we approach the central part of the periodic table.
Image: YouTube
Ionic radius and Vanderwalls radius.
The ionic radius is the radius that an ion of an element has in the ionic crystal state. In that state, the ions are so close together that the outermost electronic orbitals are in contact with each other.
On the other hand, the vanderwalls radius It is the distance at which two atoms are kept apart due to the repulsion of negative charges that exist between the electrons of each of the atoms. The Vanderwalls radius would be the radius of an imaginary solid sphere used to model the atom so it is not used much in daily practice.
Unlike what happens with density or mass, these two properties are closely related with the volume of the atom, that is, they have more to do with the number of electrons in it than with the core.

Image: SlidePlayer
Ionization energy.
Finally, another of the properties of the atom is the ionization energy, a property that tells us the energy we need to separate an electron in its ground state (other than an anion or cation) of an atom of an element in a gaseous state but it could also be defined as the force with which an electron bonds with other molecules. This property is very interesting as it allows us to get a rough idea of the ability to react of an atom of a certain chemical element. The ionization energy is higher as we remove electrons, so for an element there is an energy of first ionization, a second ionization energy, and so on and they get bigger and bigger.
As in the previous case, this property is also closely related to the number of orbitals of the element in question since, the fewer orbitals it has, the more it will cost to remove the electrons from an atom determined.
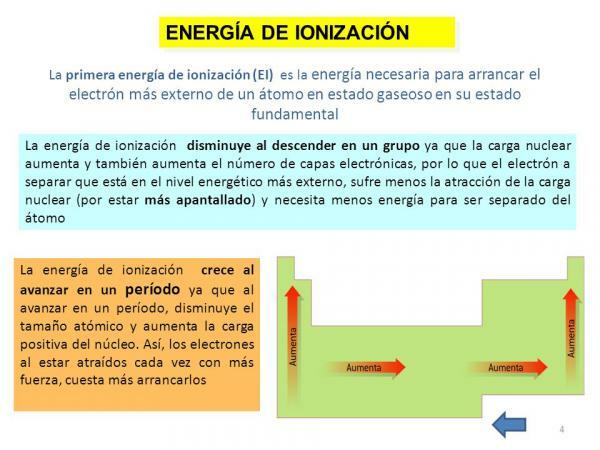
Image: SlidePlayer
If you want to read more articles similar to Atom properties, we recommend that you enter our category of The atom.