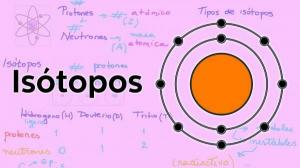
Find out what the ATOMIC NUMBER is
Matter is made up of atoms of different chemical elements. Chemical elements have different properties and characteristics that distinguish them from each other and undoubtedly one of the most important is the atomic number. The atomic number, which is usually represented by the letter "Z", represents the number of protons that a certain atom has. Atoms of the same element have the same atomic number, while atoms of different elements always have different atomic numbers.
If you ever wondered what is the atomic numberWe invite you to continue reading this lesson from a PROFESSOR to know its definition but also what implications this has for atoms.
Index
- Atomic number: simple definition
- The atomic number and the elements
- Relationship between the periodic table and the atomic number
- The atomic number and the neutrality of the elements
Atomic number: simple definition.
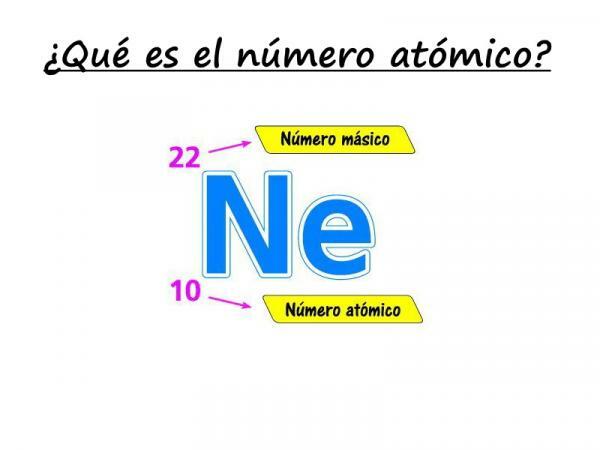
If you want to know what the atomic number is, pay attention to our explanation! The atomic number is
the number of protons that make up the number of an atom of a certain element. It is usually represented by the letter "Z" (always in capital letters), which comes from the German word zahl, which means number.Let us remember that inside an atom there are, classically, three types of particles: protons, neutrons and electrons. In the nucleus are protons and neutrons, which have the largest amount of mass in the atom. Therefore, the sum of the atomic number Z and the number of neutrons N gives the mass number A of an atom.
Sometimes in nature, we can find atoms with the same atomic number (Z), but different numbers of neutrons (N), and therefore different atomic masses. These atoms are known as isotopes. If you want to know more about Characteristics of isotopes you can consult our lesson on the subject.
The atomic number has many applications in physics and chemistry. In the following sections we will see, in addition to its main utility, what physicists and chemists have used the atomic number for.
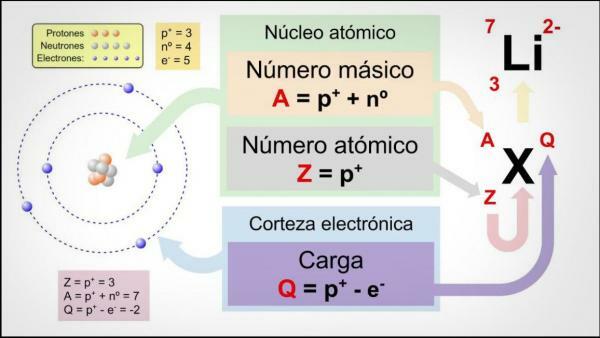
Image: Definition
The atomic number and the elements.
Now that we know what the atomic number is, let's see its uses. The main utility of the atomic number in physics and chemistry is the define the atoms of the same element. It is so important that the search for new elements is usually done using atomic numbers.
An atom can have the same number of electrons as another and not be atoms of the same element. On the other hand, if the atomic number of two atoms is the same, necessarily both atoms belong to atoms of the same element.
Atoms, in their pure natural state as chemical elements, they are in this neutral. Therefore, according to the principles of quantum mechanics, it will be the number of protons in the nucleus of the atom which determines the number of electrons it can hold in its orbitals, which surround the core. The number of electrons, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining their chemical bonding behavior.
Therefore it is the atomic number the fact that determines chemical properties of an element. For this reason an element can be defined as consistent if we have a mixture of atoms with a given atomic number.

Image: 100Cia.site
Relationship between the periodic table and the atomic number.
As we have seen before, the atomic number or number of protons in the nucleus is what really determines the number of electrons that a certain atom can have. That is why, indirectly, the atomic number determines the order of the elements in the periodic table.
If you have ever had to face the study of the periodic table of elements, you may have asked yourself, what criteria have they followed when ordering these elements? Are they randomly ordered? Perhaps according to their order of discovery? Well no, they are arranged according to the order of filling of electronic orbitals.
As we have already seen, the atomic number ultimately determines the number of electrons an atom can have. Therefore, the atomic number defines the electron configuration of the atom. This is why, indirectly, the atomic number allows the ordering of the different chemical elements in the table periodic, which begins with hydrogen (Z = 1) and continues with helium (Z = 2), lithium (Z = 3), beryllium (Z = 4), boron (Z = 5), carbon (Z = 6), etc.
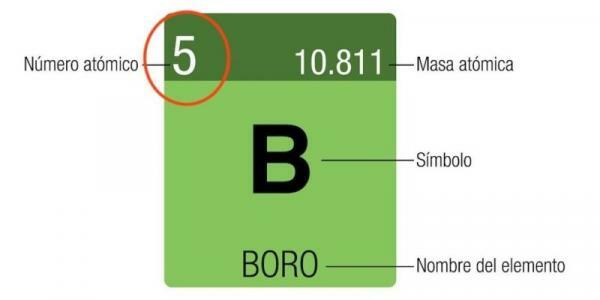
Image: Pinterest
The atomic number and the neutrality of the elements.
Normally, chemical elements are usually expressed as neutral atoms or molecules but they don't have to always be. Sometimes some atoms or molecules have more or fewer electrons than they should. In the event that the atom or molecule has the due electrons, and has no electrical charge, (electrically neutral), the atomic number will be equal to the number of electrons in the atom that can be found around the Cortex.
In other cases, the atoms may have a greater number of electrons than their corresponding atomic number, and are negatively charged by so many. These are called anions. Otherwise, the number of electrons in the atom or molecule is less than the atomic number and they will be positively charged. We would be facing a cation.
These electrons mainly determine the chemical behavior of an atom and they will be very important in determining how the different atoms or molecules are related to each other.
If you want to read more articles similar to What is the atomic number, we recommend that you enter our category of The atom.
Bibliography
- Nuclear Energy (May 20, 2019) Atomic number. Recovered from https://energia-nuclear.net/que-es-la-energia-nuclear/atomo/numero-atomico
- Recio Miñarro, J. (s.f) The atomic number and the mass number. Recovered from http://newton.cnice.mec.es/materiales_didacticos/el_atomo/zya.htm? 4&0
- Wikipedia (January 25, 2020) Atomic number. Recovered from https://es.wikipedia.org/wiki/N%C3%BAmero_at%C3%B3mico