Neutrons, Protons, and Electrons: Simple DEFINITION

Image: Preparaniños.com
The atoms are, according to classical chemistry, the structural unit of matter. That is, everything that is around us and we can perceive through any of our senses is made up of atoms. Throughout the 19th century, researchers believed that there was nothing smaller than the atom. During the first decades of the 20th century, researchers such as Thomson, Stoney or Einstein discovered that Atoms, even if they were very small, could be divided into other particles, neutrons, protons and electrons.
The set of all these particles is called subatomic particles. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will review simple definition of neutrons, protons and electrons and their differences and how they are alike.
Index
- What is the proton: simple definition
- Definition of neutron
- Definition of electron
What is the proton: simple definition.
The proton is one of the subatomic particles that is in the center of each atom(core). The protons and neutrons of the same atom group together forming the
core of atoms, so these two particles are also called nucleons. Unlike the other particles that are part of the atom, the proton has a positive charge of 1.6 × 10-19 C and is said to be very stable since the half-life of a proton can reach more than 1035 years.Besides being a very stable particle, the proton is incredibly heavy for your size: 1.672621898 × 10−27 kg, so it is 1836 times heavier than the electron but at the same time it is one hundred thousand times less than a whole atom.
As we have seen previously, atoms are not indivisible, but neither are subatomic particles. In the 1970s it was discovered that protons are composed of three quarks. Those three quarks are linked by gluons, so it is considered that protons are classified within the group of subatomic particles of baryons (particles made up of three quarks). In addition to the number of quarks they have, subatomic particles are classified according to their spin, that is, their spin; within this classification, protons are fermions since they have a 1/2 ħ spin (half-integer spin particles).
The proton is an important particle in determining some of the most important characteristics of the atoms of the different chemical elements. The number of protons in an atom determines the atomic number of the same, and with it the chemical element to which it belongs. For example, all atoms with 20 protons in their nucleus have an atomic number of 20 and are calcium (Ca) atoms.
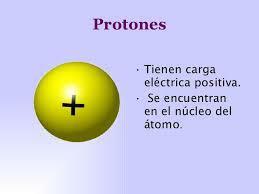
Image: Comparative tables
Definition of neutron.
As we saw earlier, neutrons are found forming the nucleus of atoms along with the protons. All atoms have protons in their nucleus except the protio, which is an atom made up of only one proton and one electron and has no neutron in its nucleus.
The neutrons and protons share some features such as your weight. The two particles have a more or less similar mass, and much greater than that of the electron. Neutrons, like protons, are made up of three quarks, which is why they are included within the baryons and they have a 1/2 ħ spin, so they are considered fermions (semi-integer spin particles).
Something that does differentiate protons and neutrons is their half-life: while the proton was very stable, the neutron is a particle very unstable and its half-life is only about 14.7 minutes.

Definition of electron.
Electrons have some characteristics that make them very different from the rest of the particles that are part of the nucleus. First of all, electrons are the only subatomic particles that can be found in two forms: free or forming part of an atom.
The second difference is in the place of the atom in which they are: the electrons are not part of the nucleus of the atom, they are not in the center, but are on the periphery, surrounding it and forming what is called Cortex of the atom. Electrons are said orbit around the nucleus, like the planets of the solar system around the Sun. According to their spin, the electrons are considered fermions since they have a spin of ± 1/2 ħ, (half-whole spin particles).
The electron is a particle with a proton-like charge (1.6 × 10−19 C) but with the opposite sign, that is to say, protons and electrons have a force that has more or less the same intensity but they have opposite sense. Also, electrons are quite stable: have a half-life of about 4.6 × 1026 years.
Something that differentiates electrons from the other subatomic particles that we have seen above is that they are the only ones that, to date, have not been proven to consist of units smaller. The electrons would in fact be leptons, particles that are currently believed to be the true elementary particles and are not made up of other smaller elements. Electrons would be an elementary particle, while protons and neutrons are subatomic particles (smaller than the atom) but not elementary.

Image: Slideshare
If you want to read more articles similar to Neutrons, Protons, and Electrons: Simple Definition, we recommend that you enter our category of The atom.
Bibliography
- Belmonte, A. (June 25, 2019) Subatomic particles: definition and characteristicsMaría del Mar (October 2, 2018) The atom - What it is, structure and composition.
- Prepara Niños (n.d.) What Is The Atom: Explanation for Children.