Types of MUSCLES of the human body

The human body is made up of more than 650 muscles And, as you can imagine, these are very different. The muscles of the human body can have different structure, movement, size, shape, location, function, etc. but all of them are important.
In this lesson from a TEACHER we will look at the main types of muscles of the human body according to different classifications. These classifications are used in different areas of life, you will surely find them very interesting!
Index
- Types of muscles according to their microscopic morphology
- Types of muscles according to their shape and size
- Types of muscles according to their movement
- Types of muscles according to their group action
Types of muscles according to their microscopic morphology.
One of the ways to classify muscles It is according to how they look under the microscope. The muscles They are made up of muscle tissue that, seen under a microscope, can look different:
- The striated muscle It is one that, seen under the microscope, has striations or horizontal bands. This muscle, generally, is of voluntary action and is the one that forms, for example, the muscles of our arms. Striated muscle can also be called voluntary or skeletal. The contraction of these types of muscles, despite being very fast, is eliminated very soon since they are muscles that tire quickly and cannot withstand sustained contractions.
- The smooth muscle It is one that, seen under the microscope, does not have the bands that are observed in striated muscle. Unlike the previous one, smooth muscle is involuntary and is what forms, for example, the walls of the viscera and blood vessels. Unlike the previous ones, their response is not as fast but they can maintain the contraction for a longer time.
- A very special kind of smooth muscle is he heart muscle, that is only found in the walls of the heart. The heart muscle or myocardium has intermediate characteristics: it is made up of cardiomyocytes, which seen under the microscope are striated, but their control is involuntary. In addition, cardiomyocytes are branched, something that does not occur in other types of muscles and allows them to connect with each other and form a network that facilitates the coordinated contraction of the myocardium.

Image: Google Sites
Types of muscles according to their shape and size.
In addition to their view from the inside, the muscles also they can be classified according to how we see them from the outside, without the aid of microscopes. According to their size and shape, in the human body we can distinguish four groups of muscles:
- Long: they are muscles with one of their axes longer than the other. They are usually very strong and powerful muscles. Within the long muscles there are subgroups, depending on their shape; For example, the biceps is a long, fusiform muscle, while the rectus abdominis is long and flattened.
- Short: short muscles are those that, regardless of their shape, are very short in length. They are, for example, the muscles that are part of the head and face such as the frontal muscle, the plateaus, etc.
- Orbicular: they are more or less circular muscles since they surround some structure, normally circular. Some important orbicular muscles are located around the mouth and the eyelids.
- Widths: are those in which all their axes have approximately the same length. They are generally flattened and thin. An example of a latissimus muscle is the latissimus dorsi of the back, and many are found in the trunk.
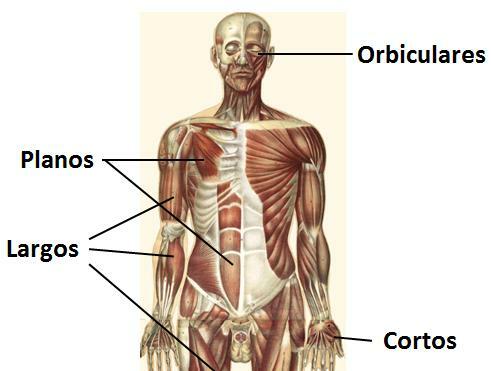
Image: Add
Types of muscles according to their movement.
The muscles of the extremities are usually classified, rather than by their shape or size, by the type of movement they make. According to this there are six different types of muscles:
- Flexors: they allow the flexion of different parts of the body, that is, that we bring a structure closer to the body. For example, the palmaris maximus allows flexing of the wrist and retracting it onto the wrist or the long supinator, which allows flexion of the elbow.
- Extenders: they allow the extension of the extremities, that is, that the structure moves away from the trunk. For example, the fingers of the hands have extensor muscles that allow them to be pulled away by stretching them back.
- Pronators: they are those that turn the extremities (for example, the hands, the feet or the hips) inwards. An example is the pronator quadratus muscle, found in the forearm, which is responsible for that at rest, the elbows have a pronated position, that is, slightly flexed towards within.
- Supinators: they are those that allow the limbs to be tilted outwards. An example of a supinator muscle is the biceps.
- Abductors: they are responsible for moving the extremities away from the central axis of the body. An example is raising an arm to the sides. Another example is the muscles that make up the glutes: gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus.
- Adductors: these bring the extremities closer to the central axis of the body. Example: place the elbow at the level of the navel or the pectineus muscle, in charge of moving the thigh towards the body and allowing its rotation towards the center.

Types of muscles according to their group action.
Muscles are normally attached to each other or to other structures and perform a coordinate function with these. That is why, often, we are much more interested in seeing how a certain group of muscles moves than how each one moves in isolation. Therefore, muscles can also be classified according to the movement they perform, as a group, with other adjacent muscles, in:
- Agonist muscles: All the muscles of the group or set follow the same course and allow us to carry out the same movement.
- Antagonistic muscles. They are those groups of muscles in which there are two types of opposite or opposite movements. For example, when an agonist muscle contracts, the antagonist relaxes and vice versa.
- Synergistic muscles. They are those muscles that indirectly allow the muscle group to perform the movement correctly. Its function is similar to that of agonists, but unlike these, it would not be so involved in the movement itself, but would have a more stabilizing and controlling role in it.

Image: Educarex
If you want to read more articles similar to Types of muscles of the human body, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Ortiz, J N (January 20, 2019) Types of muscles and their function. Training world. Recovered from: https://mundoentrenamiento.com/
- Visible Body (s.f) Three types of muscle tissue: Skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle function. Recovered from: https://www.visiblebody.com/es
- ICARITO (s.f) Types of muscles. Recovered from: http://www.icarito.cl/



