FLAT bones: function and characteristics
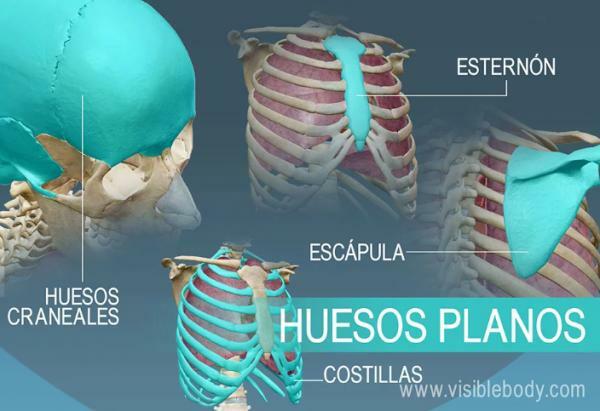
Image: Visible Body
The body of an adult has 206 bones They include bones as different as the ribs, the bones of the ear, the bones that make up the skull, or the bones of the extremities. To study them, bones are classified into five main groups: long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid. In this lesson from a PROFESSOR we will take care of studying flat bones, those bones in which their width and length predominate as opposed to being very thick. If you want to know more about flat bones, its characteristics, functions and a list with examples of flat bones, read on!
The bones of the human bodythey can be very varied and have very different characteristics depending on where they are located and their function. Although they have very different characteristics, researchers have been able to classify the bones of the human body according to their appearance and internal characteristics into five groups: long bones, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid.
The flat bones are those who are formed by thin sheets of spongy bone tissue,
inside, covered by compact bone tissue. They are similar to a cream-filled cookie, in that the outer layers are hard and the inside is "softer" or fluffier. This is because cancellous bone, unlike compact bone, has tiny holes filled with air and fluid with different functions.In flat bones, unlike in others, what predominates is its surface. As we will see later when we discuss the functions of flat bones in the body, it is important that these bones have a lot of contact surface but it is not important that they are very thick or thick.
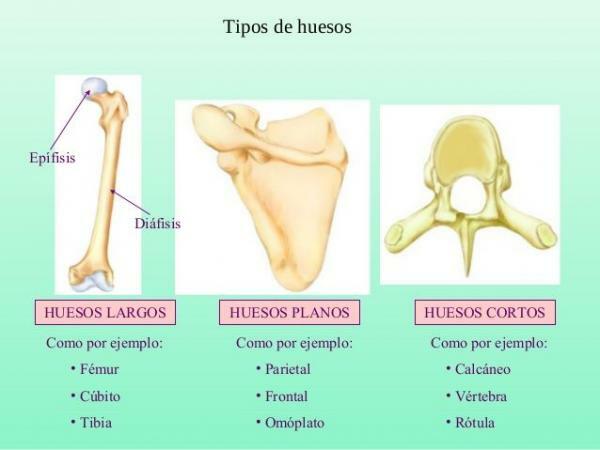
Image: Pinterest
In this section of the lesson on the flat bones of the human body we will review 5 bones or groups of flat bones with important functions in the human body:
1. The plane bones of the skull
The skull or cranial vault is made up of eight flat bones: four odd ones centered on the midline (frontal, ethmoid, sphenoid and occipital) and two bilateral paired bones (temporal and parietal). The function of these bones is to protect the brain from possible blows, mainly but they also give structure to the eye sockets and the nostrils.
The skull is made up of different bones to facilitate childbirth and brain development during the first months of life. During delivery, the baby has to pass through the mother's hip bones through a small space called birth canal; To be able to cross it, the bones of the skull are not totally hard, but rather they are somewhat moldable (they are not completely ossified) in addition to not being completely fused. At birth, the brain continues to develop and the flat cranial bones become hardened, ending the ossification and finally they merge each. The only remnant that remains in the adult of this process are the lines of union between the bones, called sutures.
2. Shoulder blades
The shoulder blades or scapulae are a pair of flat, triangular, slightly curved bones that meet at the top of the shoulders, connecting each of the arms to the clavicle.
The function of the scapulae is not so much to protect the back of the back, but rather to be the insertion point of important muscles of the back such as the rhomboids, the rotator cuff or the serratus. These muscles allow us to rotate the arms, the movements of the upper back or even to help other muscles when we pick up very heavy objects.
3. Sternum
The sternum is a small, tie-shaped bone found in the upper center of the chest. This bone is connected to the ribs: with the first seven pairs of ribs it joins directly while with the pairs 8, 9 and 10 it does so through cartilage. The set of the sternum and the ribs make up the rib cage.
The sternum, like the ribs, is responsible for protect vital organs like the lungs or the heart, but at the same time it gives a certain elastic capacity to the rib cage, which allows its expansion during inspiration and respiratory expiration.
4. The ribs
The ribs are twelve pairs of bones that connect at one end to the spinal column and at the other with the sternum (directly or through cartilage).
The main function of the ribs is organ protection of the upper part of the thorax: lungs and heart, but by extending a little below it, it allows them to also act as a protective shield for the liver and spleen.
5. The bones of the pelvis
The pelvis is formed, in addition to other bones, by three flat bones: the ilium, the ischium and the pubis. During adolescence, these bones allow the leg bones to grow, and once height growth is complete, these bones are firmly joined or welded together.
The pelvis or hip is a structure that serves both as point of attachment of different muscles as structure of organ protection as important as the bladder or the reproductive system (male and female).

Image: Human Skeleton


