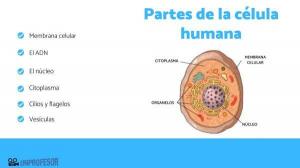
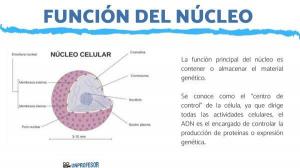
Eukaryotic and prokaryotic transcription differences
In this video I will explain transcription differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes.

Transcription differences:
In prokaryotes, the RNA So good point messenger is transcribed, it is directly translated into amino acids. In eukaryotes, the process is slower; First, a pre-messenger RNA is transcribed and a maturation process occurs by which the messenger RNA is obtained to pass to the amino acids.
The DNA of prokaryotes is very packaged unlike the DNA of eukaryotes, which is also associated with histones.
On prokaryotes, there is only one type of polymerase. In contrast, in the RNA of eukaryotes, there are three polymerases (rRNA, mRNA, tRNA).
In prokaryotes, both transcription and translation take place in the cytosol, unlike eukaryotes, which transcription takes place in the nucleus and translation in the cytosol.
In prokaryotes, each gene can make several chains of amino acids (polycistronics). On the other hand, in eukaryotes, the opposite happens, a gene, a chain of amino acids (monocistronic).
In the video you will be able to understand better transcription differences between eukaryotes and prokaryotes. In addition, if you are not sure you can continue practicing with problems of this type you can do the printable exercises with their solutions that I have left you on the web. Good luck in your studies!