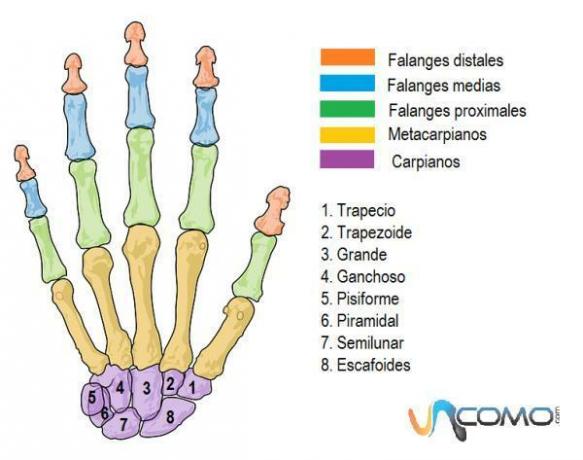
LIST with all the names of the BONES of the wrist

Image: Knowing is practical
One of the great advantages of human evolution was bipedalism, which allowed us to stand on two legs. With this, we obtained a great advance: the final part of the front legs, which we call hands, were left free and allowed us to interact with the environment. The hands allow us to clean ourselves, write, pick up objects, eat and countless other things in our daily lives. In the hands we can differentiate three parts main: fingers, palm and wrist. The wrist is a set of bones and ligaments that allow the rest of the hand to be joined and articulated with the arm, giving mobility but also holding it firmly. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will review all the names of the wrist bones so that you know what our bone structure is like.
Index
- How are the wrist bones organized?
- Scaphoid, one of the wrist bones
- Lunate bone
- The pyramidal bone of the wrist
- Pisiform
- The trapeze
- The trapezoid
- The big bone
- The hamate bone
How are the wrist bones organized?
The doll, or carpus As it is called in anatomy, it is located at the base of the hand and is made up of a total of 8 bones. These eight bones are distributed in two rows. The distal row, closer to the ulna and radius (the bones of the arm), is made up of the bones: trapezoid, trapezoid, large and hooked.
The proximal row, closest to the palm of the hand, is made up of the bones: scaphoid, lunate, pyramidal and pisiform. While the ligaments of the proximal row are looser, and allow us to have greater mobility, the ligaments of the distal row, closer to the hand, are more rigid and give support to the bones of the palm and fingers.
In the following sections we will see the characteristics of each one and its function within the doll. If you want to know more about each of these little bones, we invite you to keep reading!
Scaphoid, one of the wrist bones.
Bone scaphoid It is the first of the wrist bones in the proximal row, closest to the arm. This bone is on the radial border of the wrist and is directed towards the thumb on the side. It is the largest bone in the proximal row and is slightly concave in shape. In the center of this concavity the large bone articulates while on the opposite side, the convex, it articulates with the radius.
Therefore, How to find the scaphoid bone on an x-ray? Too easy! You will only have to look for the radius, the largest and widest bone in the arm. Of the two carpal bones that articulate with it, the one on the outside of the wrist will be the scaphoid and the next will be the lunate bone, which we will talk about next.
In this other lesson we will discover what are the parts of human bones so that you know our anatomy better.
Image: Tulesion.com
Semilunar bone.
Bone semilunar it is the second carpal bone of the proximal row. As we have discussed previously, it articulates with the radius on one side, with the scaphoid on the other, with the large bone and the hamate bone on the other, and with the pyramidal bone on the last of its sides. As its name suggests, the lunate bone is shaped like a crescent, specifically a crescent moon.
As we saw previously, to identify the lunate bone in an X-ray we will only have to find the radius, with which two carpal bones articulate. At the end we will find the scaphoid and followed by it, the lunate bone.

Image: SlidePlayer
The pyramidal bone of the wrist.
Bone pyramidal It is another of the names of the bones of the wrist that you should know. It is the third bone of the proximal carpal row. In this case, the pyramidal bone has that name because of its shape: it looks like a three-sided pyramid. This bone articulates mainly with the piriformis bone, which we will see below.
If you want to find this bone on an X-ray, it will be difficult since it is hidden under the piriformis. If you locate the ulna, the thinnest arm bone, you will see that it articulates with two small bones, superimposed: the pyramidal bone is below (and we will not see it well) and the pisiform, by on.
Pisiform.
The fourth bone of the proximal carpal row is the pisiform. Bone pisiform It is located on the ulnar edge, that is, it articulates with the ulna and is at the end of this bone (a differential of the scaphoid, which is said to be at the end or radial edge). This bone has a very peculiar shape since all its edges have a different shape: one oval, another rounded, another concave and another convex.
Where to find the pisiform bone on an x-ray? Identify the ulna, the thinnest bone in the arm. Articulating with it you will find two small bones, which are part of the carpus, one on top of the other. The bone that is above, and which is slightly larger, is the pisiform while the one below, and has the shape of a pyramid, is the pyramidal bone.

Image: Slideshare
The trapeze.
Already in the second row, the distal row, closer to the palm of the hand, we find the trapeze. The trapezius is the first bone in the distal row and is located at the radial end, surrounded by the scaphoid bone and the trapezoid bone. It articulates with the scaphoid, the first bone of the proximal carpal row, the trapezoid bone, and the first metacarpal (part of the wrist bones).
To identify it on an x-ray, it will not be easy since it is hidden behind the trapezoid bone. We will have to identify the radius, the widest bone of the arm; glued to this we will find the scaphoid, at the end of the carpus, in the first row and in the second row, at the end and hidden under the trapezoid, we find the trapezium.
The trapezoid.
The trapezoid It is the second bone of the distal row of the carpus. This bone articulates on one side with the scaphoid, on the other with the trapezius and on the other with the second metatarsal, which is part of the palm of the hand. As its name suggests, this bone has a trapezoid shape and to identify it on an x-ray we will have to follow the same steps as for the trapezius.
The big bone.
The big bone It is the third bone of the distal carpal row. The name corresponds to its reality since it is the largest carpal bone. This bone is in the center of the bones that form the wrist and articulates with the scaphoid and lunate on one side, the trapezoid on the other and the hamate on the other.
On the ventral surface, the lower part of the wrist that we support when writing, serves as a connection to numerous ligaments while in the distal part it is attached by means of three projections (called ridges) to the metacarpal 2, 3 and 4. Due to its large size and central position, the large bone is easily identifiable on radiographs and models.

Image: Slideshare
The hamate bone.
The hamate bone is the last bone of the distal carpal row and is located at the ulnar end. This bone is embedded in one of the faces of the lunate bone and articulates with the lunate bone, the great bone, and metacarpals 4 and 5.
To identify it, we will only have to identify the large bone and, on one of its sides, we will find a single bone somewhat smaller but much larger than the others, this is the hamate bone.
If you want to read more articles similar to Names of wrist bones, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Physihealthy (October 3, 2017). The eight bones of the carpus. Recovered from https://fisiosaludable.com/
- Topographic Anatomy. Carpal bones. Recovered from https://www.anatomiatopografica.com/