IRREGULAR bones: function, characteristics and examples
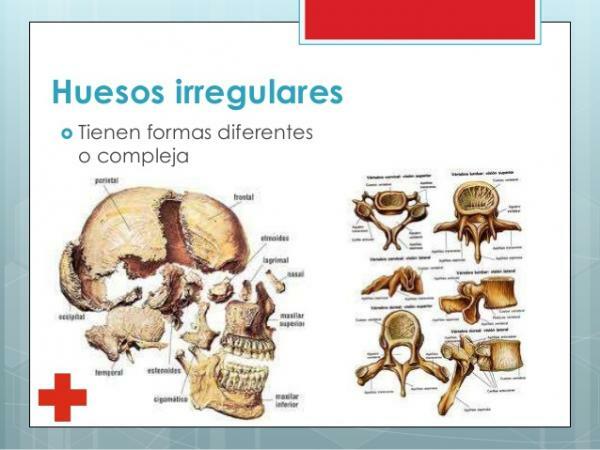
Image: Tasks App
The skeleton of an adult has a total of 206 bones! These bones have very different shapes: there are elongated bones, like those that make up the bones of the arms and legs, flat bones like those that make up the skull, etc. The science that studies bones, called osteology, divides the bones of the human body into 5 groups or categories: long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones, bones sesamoids. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will see what irregular bones look like and a list of examples.
The irregular bones They are those that, due to their shape, cannot be classified in any other group (long, short, flat or sesamoid). To make its definition clearer, we have to take into account that bones are classified according to their shape into 5 groups:
- Long bones. They are characterized by being long, narrow and having a fairly thick outer layer. They are the bones that form, for example, the arms and legs.
- Short bones. They are bones in which none of the dimensions predominate over the others, that is, they have a more or less cubic shape. Some examples are the bones that make up the wrist or fingers.
- Flat bones. They are planes in which their width and length predominate, while they have little thickness. An example of flat bones are those that make up the skull.
- Sesamoid bones. Sesamoid bones are small accessory bones, that is, they can be found in some people and not in others, in various locations. They are normally part of joints such as the knees.
- Irregular bones. Finally, we find the group of irregular bones. This group is a "disaster drawer" in which all the bones that do not include the rest of the groups are included, that is, those that have "strange shapes". A typical example of irregular bones is the ribs, but later we will see a list of irregular bones distributed throughout the body.

Image: Slideshare
Irregular bones have different functions. As we saw previously, they are a very varied group of bones made up of bones with very different shapes and that are located in very different places in the human body.
Most irregular bones have these functions:
- The function of give mobility since they are part of structures such as the feet or hands
- But there are also irregular bones with protective function, which function as an insertion point for powerful muscles or provide support of a different kind.
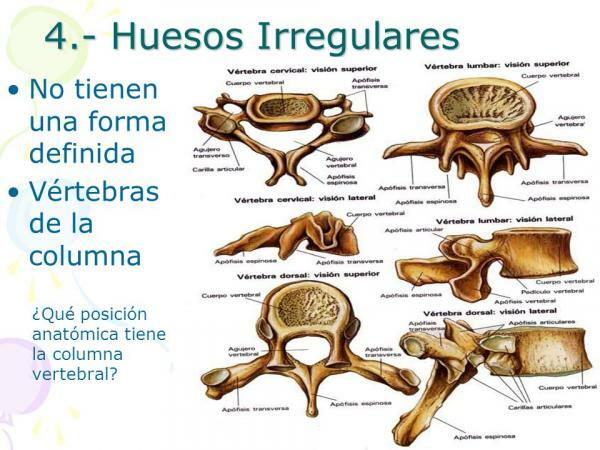
Image: Answers.tips
The human body is made up of approximately 33 irregular bones. In this lesson from a PROFESSOR we propose a list of 10 irregular bones and the most important functions of each of them:
1. Vertebrae
The best known irregular bone and typical example of irregular bone are the vertebrae. In addition to being an irregular bone, with a very different shape from the rest, the vertebrae of the different parts of the spine have different characteristic shapes.
The vertebrae are responsible for supporting the body, protecting the spinal cord -which is part of the central nervous system-, it is the point of insertion of many muscles, etc.
2. The sacrum
The sacrum contributes to the formation of the lower spine and pelvis. It is responsible for transmitting the weight of the body to the pelvis, supporting the weight of the upper part of the body when standing, provide insertion points for locomotor, postural, etc. and protect part of the structures contained within the pelvis.
3. The coccyx
The coccyx, for its part, is a small vestigial bone that supports and supports ligaments and muscles such as the gluteus maximus. In addition, it supports part of the body weight when we are sitting.
4. Ear bones
There are three small bones of the ear: anvil, stapes and hammer. These bones are small bones that are found inside our inner ear, in the eardrum box and that are responsible for the transmission of sound in the innermost part. They are bones of very small size and with strange shapes that are reminiscent of the instruments that give them their name.
5. Hyoid
The hyoid bone is a single, U-shaped bone that is located in the neck, below the tongue, and before the thyroid gland. The hyoid supports the tongue, which is located above it, and supports the larynx that hangs below it and transmits the force of the muscles that help open the jaw. For this reason, despite the fact that it is a small bone that normally goes unnoticed, a displacement of it can cause problems with chewing, swallowing and / or phonation.
6. Tear bones
The vast majority of the bones in the face are irregular bones. The tear bones or unguis They are paired bones that are shaped like a fingernail. They are thin and consist only of compact bone tissue. They contain a tear hole, through which the tear duct passes.
7. Palatine bones
The palatine bones are found on both sides of the vomer bone and are responsible, along with other structures, for causing resonance when we speak.
8. Maxilla
The maxillary bone is a very important irregular bone of the viscerocranium. It forms the upper part of what we commonly call the mouth and is involved in important functions such as chewing, phonation, taking air, etc.
9. The ethmoid
The ethmoid is a unique irregular bone, that is, each of us only has one in our body. This bone separates the nasal cavity from the brain and is located in the upper part of the nasal cavity, between the two orbits, of which it is a part.
10. Vomer and nasal bones
The vomer bone is located at the back of the nasal septum, which divides the nose into the left nostrils and right while the nasal bones are a pair of bones that, as their name suggests, are part of the nose. Specifically, they are part of the root and the back or bridge of the nose.
If you want to read more articles similar to Irregular bones: function, characteristics and examples, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.