All BONE FUNCTIONS

what are bones? To understand the bone functions, we must first know what some of its characteristics are. Bones are organs made up of various types of tissue. The main tissue and, therefore, the most abundant in these organs is bone tissue, made up of bone cells. Only the Vertebrate animals They have these types of organs.
The bone structure is characterized by being formed, in addition, of cartilaginous tissue and bone marrow. The surface of the bones is lined with cartilage called periosteumThis fulfills the function of protecting, nourishing and intervening in the growth of the bone. Between the different layers we can find blood and lymphatic vessels and nerves.
Then we invite you to read the following lesson from a TEACHER: What are the functions of the bones?
Index
- Characteristics of bone tissue
- bone functions
- Bones are constantly changing
Characteristics of bone tissue.
As we saw earlier, the main bone tissues is the famous bone tissue. Before starting with the functions of the bones, we tell you what the characteristics of this tissue are.
The woven bone is mainly composed of water, collagen fibers and mineral salts. The most abundant mineral salts that compose it are: hydroxyapatite (calcium phosphate) and calcium carbonate, they are the ones that give hardness and flexibility to the bones.
Bone tissue forms thin structures called lamellae, and according to your disposition we can sort out to the fabric in:
- Compact: It forms the outer part of all bones. The lamellae are arranged regularly and form thick layers.
- Haversian: It is found in the diaphysis of the long bones. The lamellae are arranged as concentric rings around central channels, in these channels are the blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves.
- Spongy: It constitutes the epiphysis of long bones and the interior of most bones. The lamellae are irregularly arranged, forming holes where the red bone marrow.
bone functions.
The bones meet forming the skeletal system in vertebrate organisms. Its functions are many, among them we can highlight the following:
Medium
Bones are the support for soft tissues and the fulcrum for most skeletal muscles.
Protection of internal organs
Bones are found protecting the internal organs of the body. An example of this is the rib cage, which with the ribs surrounds the lungs and heart, or the skull that protects the brain.
Mobility
Mobility is another of the main functions of the bones. The skeleton is part of the locomotor system of the body. Being the support of the muscles, they accompany the body movement
Homeostasis
Bone tissue has the ability to store or accumulate certain substances as needed, it can store, for example, certain minerals such as calcium and phosphorus, necessary for muscle contraction and other functions. When the body requires these minerals, they are released by the bone tissue into the bloodstream to be redistributed.
blood cell production
In some types of bones we can find the spongy tissue, within the cavities that are formed in this type of tissue, we can find the red bone marrow.
Did you know? Red bone marrow is a special type of connective tissue that contains red blood cell precursor stem cells, which means is that in this place blood cells such as red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
energy reserve
in the calls long bones we can find a channel inside, this channel contains the yellow marrow (known as "caracú"). This tissue is mainly made up of adipose tissue, which means that it stores fat or lipids, which is why it is considered an energy reserve.

Bones are constantly changing.
Bones are in constant motion this means that they are constantly destroying and renewing themselves.
Bones are made up of various cells: osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts. The cells that intervene in the process of destruction of bone tissue are the osteoclasts, these are forming channels inside. On the other hand, we have the osteoblasts, which are the cells that will "fill in" these channels, manufacturing "new bone".
Bone turnover is essential for the proper functioning of the organism, since as we mentioned above, thanks to this mechanism They release minerals, such as calcium, into the bloodstream to be transported and used in other parts of the body. body. In addition, bone turnover is crucial to maintain other types of bone functions, such as support, thanks to the fact that in this process its resistance and flexibility are renewed.
Osteoporosis
when there is one intense activity of so-called osteoclasts, excessively decreases the mass of bone tissue and thus increases the risk of fractures. This can begin to occur in the adult stage of some people, women are more predisposed to suffer from this condition.
Therefore, it is important to achieve good bone development during childhood and youth, incorporating the necessary nutrients such as calcium and vitamin D that favors the absorption of this mineral that we incorporate with food.
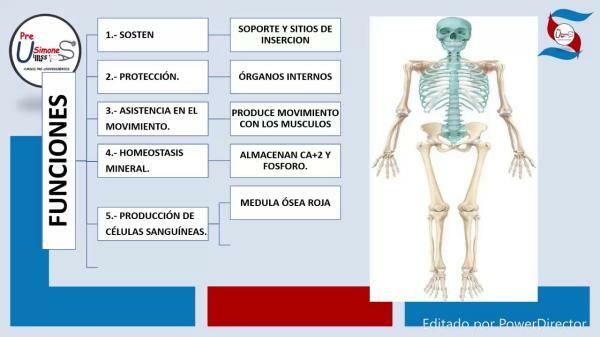
Image: Youtube
If you want to read more articles similar to bone functions, we recommend that you enter our category of biology.
Bibliography
- Adúriz-Bravo, A.; Bardi, M. G.; Busts, d. EITHER.; Fried, D. J.
- Hardmeier, P. m. and Suares H. g. (2006). Biology. Human anatomy and physiology. Genetics. Evolution- Perspectives Series-. Editorial Santillana. Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, Argentina.