What are CONVERSION factors and examples

In a new lesson from a PROFESSOR we will see what are conversion factors and examples. We will start by reviewing the meaning of magnitude, then the concept of unit system, to finish with the conversion factors, their meaning and some examples. Let's start!
Index
- What are conversion factors and examples
- Characteristics of conversion factors
- What is a magnitude?
- What is a system of units?
- multiples
- submultiples
- Examples of Conversion Factors
What are conversion factors and examples.
Conversion factors are a mathematical operation which is used to make unit changes of the same magnitude. It is also used to calculate equivalences between multiples and submultiples of a certain unit of measure. In other words, a conversion factor is an account that It allows us to express a measure in different ways.
Conversion factors allow us to use a quantity and present it in different units. For this we need know the equivalence that exists between them.
These conversion factors are built as a fraction with said equivalences, in order to be able to eliminate that unit that we want to replace.
Taking this into account, conceptually, the conversion factors are equal to unity, so when multiplying them by a quantity, this is not altered.
Example of conversion factors
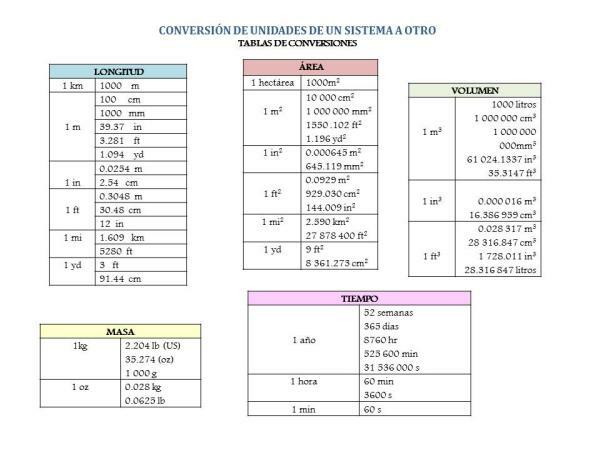
As for example 1km/1000m, we know that 1 km is equal to 1000 m. This conversion factor allows to express in kilometers a quantity established in meters by means of a multiplication. If we wanted to express, on the contrary, a quantity in kilometers in meters, the conversion factor would be inverting the equivalence, that is, 1000m/1km.

Characteristics of the conversion factors.
Here we leave you a review of the main ones characteristics of the conversion factors:
- It is a number or fraction that multiplies another.
- It is a division.
- Both the numerator and the denominator equal the same thing.
Conversion factors are used to express a measure in several different ways. That is, it allows us to know how much a measure is equivalent to.
This is very useful in everyday life because not all countries use the same units of measurement. In general, different units of measure are used for length, mass, or volume.
They are also useful for measuring solid and liquid elements or in different states, such as how many kilos is equal to a liter of water, or the equivalence between two different measurement systems such as how many kilometers are equivalent to a mile.
What is a magnitude?
In order to understand what conversion factors are, it is necessary to review some key concepts such as magnitudes and unit systems.
When we talk about magnitude we refer to the quality of a body that can be measured, that is, measure of something according to a certain scale. Magnitude is the property of bodies that can be measured, such as size, weight, length, etc
So magnitude is anything that can be measured that we can represent with a number and that can be studied. The kindness of a person cannot be measured, so sciences like physics will never study kindness, love, goodness, etc. since they are not magnitudes.
For each magnitude we have to define a unit, this is done through the measurement process where we assign numbers or values to those units. The measure is the number that accompanies the unit.
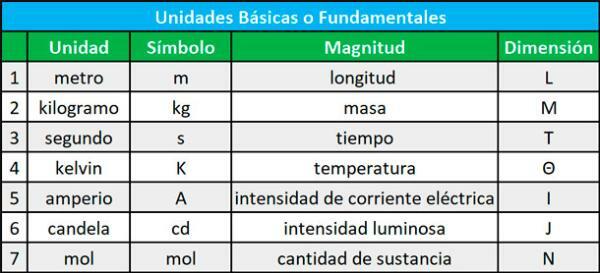
In physics some were established fundamental quantities and they are:
- Length
- Mass
- Time
- Temperature
- Electric current intensity
- light intensity
- amount of matter

What is a system of units?
Each fundamental quantity that we mentioned above has a fundamental unit defined in the International System of Units and the rest are derived from them.
Are fundamental units are:
- Unit
- Length: meter
- Mass: Kilogram
- Time: Second
- Electric current intensity: Ampere
- Temperature: Kelvin
- Amount of matter: Mol
- Luminous intensity: Candela
multiples.
The multiples are the prefixes that are placed in front of the unit and are used to multiply it by unity followed by zeros. The most common are:
- Deca (da): x 10
- Act (h): x 100
- Kilo (k): x 1,000
- Mega (M): x 1,000,000
- Giga (G): x 1,000,000,000
- Tera (T) x 1,000,000,000,000
submultiples.
Submultiples are the prefixes that are used in front of the unit and Divide it by one followed by zeros. The most common are:
- Say(d): x 0.1
- Centi (c): x 0.01
- Milli(m): x 0.001
- Micro (u): x 0.000001
- Nano(n): x 0.000000001
- Peak (p): x 0.000000000001
Examples of conversion factors.
To finish this lesson, we are going to leave you with some examples of conversion factors.
Frequent examples of the use of conversion factors are:
- Currency exchange: euros, dollars, pesetas, pounds, pesos, escudos...
- Measures of distances: kilometers, meters, miles, leagues, yards...
- Measures of time: hours, minutes, seconds, centuries, years, days...
- Changes in speeds: kilometer/hour, knots, light-years, meters/second...
concrete example.
- We live in Argentina so our currency is Argentine pesos. We want to travel to Europe and we have to convert our pesos to euros.
- The flight to the United States lists the number of miles we flew, but we want to know how many kilometers it equals.
- We are going to watch a movie that lasts 145 minutes but we want to know how many hours we need for it.
- We calculate the speed with which a car travels a highway but it is indicated in meters/seconds, but we want to know it in kilometers/hour.

If you want to read more articles similar to What are conversion factors and examples, we recommend that you enter our category of Algebra.



