What are NEOLOGISMS

Languages are not static. The interaction between different cultures, the mixture between languages and the need to give names to new objects and circumstances allow our language to be constantly updated. In this lesson from a teacher we will see what are neologisms with examples and how they change our language by introducing new words.
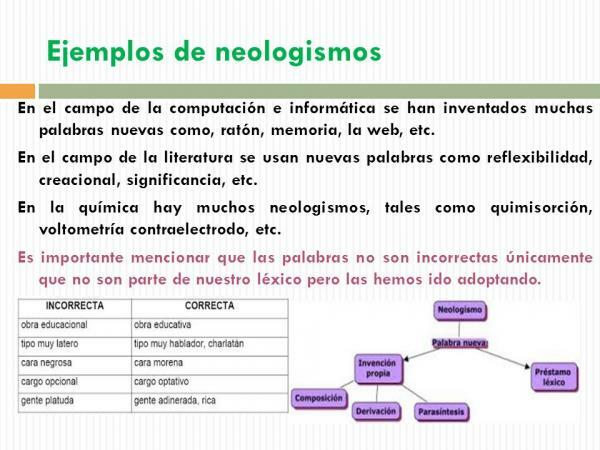
According to its etymology, the word neologism comes from the Greek composed of the prefix "neo" which means new and the word "logos" which means word. Because of this, neologisms are understood as a variation or a new word that is introduced into a language. They usually arise from phenomena related to scientific and technological discoveries, changes or revolutions social, the introduction of concepts or theoretical terms, as well as the mixture between two different languages or fashions cultural
In the specific case of Spanish, most of its neologisms have come from English or French. An important point of this linguistic phenomenon is that it shows that the creation of language lies in its use. In this way, according to Víctor Manuel Martín in his text
About neologisms, there are two ways in which they are introduced into the language:- General Neology: It occurs when a new word is introduced into the common vocabulary. It is an exercise that highlights the creativity of language in its social use. "The speaker creates a word at a specific moment without realizing whether that word already belongs to the language or not." This means that regardless of the dictionaries or the Royal Spanish Academy ruling that there is a new word in the language, it is the concurrent use that people give it that introduces it into the lexicon.
- Specific neology: it has to do with the technical nature of the language. It happens when within science or a specific discipline it is necessary to introduce a new term to name a discovery, theory or concept. As Martín points out, “it is usually planned, it is referential because it is necessary to name a new referent”.
As we pointed out in the previous section, neologisms not only change the language in terms of the pronunciation or construction of new ways of saying words that already exist in the language. The influence of foreign languages, the introduction of suffixes or prefixes, the mixing of words or the addition of terms changes and leads to new meanings. This has allowed a typology of the various linguistic forms to be created in which they are created. Now that we know what neologisms are, let's dive into their main types.
Pre-fixation
Occurs when a prefix (added to the beginning of a word) to an existing term. For example:
- Add the prefix "ex" to the word "boyfriend": ex-boyfriend.
- Add the prefix "a" to the word "political": apolitical.
- Add the prefix "co" to the word "author": co-author.
- Add the prefix "para" to the word "normal": paranormal.
- Add the prefix “ultra to the word“ grave ”: ultratumba.
Suffixation
The suffix It is just the opposite of the prefix, it is placed at the end of the word to add or give it a new meaning. Among the most common we find:
- Add the suffix "ism" to words like: nationalism, communism, surrealism, etc.
- Add the suffix "ito" to words like: little book, little path.
Composition
As the word indicates, a neologism is created when we compose it or form it with two existing words. It is also given by taking a phonological element of a word and putting it together with another:
- Match the words pint and labrios: pintlips. This also happens with the term: pintfaces.
- When we compose the words coffee and book: coffeebook. We found the same case with: coffeetheater.
- The derivation of narco of narcotics with trafficker: narcotrafficker.
- Unite the cardinal south with Korea: southKorean.
Syntagmation
It is when a term is constructed with two words and they generate a meaning that only makes sense when both words are together. If we remove any of them, it loses its meaning:
- Social agent: groups or institutions that are involved in the socialization processes.
- Political subject: the individuals involved in power relations in a society.
- Without papers: person in a condition of illegality in a foreign country.
- Domestic violence: physical or psychological violence exerted within the family environment.
Shortening
It is when a word is limited or reduced and although a new word is created it has the same meaning as its original word. For example:
- Pen that comes from a ballpoint pen.
- Photography photo.
- Hetero that comes from heterosexual.
- Narco, as we saw in the first example of prefixation that comes from a drug trafficker.
Neology by loan
You may have heard of the Anglicisms or foreigners, since the neologism by loan occurs when a term of a foreign language is incorporated in the own one. In the case of Spanish, due to the influence of English and the globalization process in the West, this has become an increasingly common phenomenon. Let's see some cases:
- E-mail.
- Marketing.
- Mall.
- Hashtag.
- Vintage
- Sponsor.
- Tablet.