Verb to be conjugated in Spanish
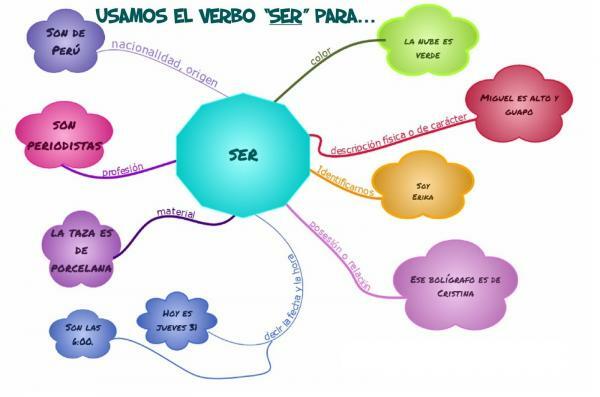
Image: Spanish exercises
The study of verb SER and the verb ESTAR It is one of the most complex issues in Spanish grammar, especially for foreign students in whose mother tongue there is no such difference between the two verbs. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will study in depth the verb to be conjugated in Spanish so that you know all the verb forms of that word and, thus, understand how it can be used correctly.
Before we start looking at the conjugation of the verb SER, let's briefly review what are the most general uses of this verb. In Spanish, we use the verb SER to:
- The permanent, essential, or inherent characteristics: I am taller than my brother.
- The location of an event or event in time and space: The classic is Thursday; Pablo Alborán's last concert is in Granada.
- The dates, seasons of the year and hours of the day: Today is Wednesday; Tomorrow is May 1; Is August; What time is it? It is 6pm.
- buildings passively: Red team was defeated by blue; The food is made by my mother; Thieves are caught red-handed.
- Professions or jobs: My father is a doctor; I am engineer.
- Information related to the price of things: How much is it? They are 15 euros.
- To indicate the material from which it is made an object: My necklace is made of gold; This bracelet is silver.
- To point out the origin of a person: I am Spanish; My best friends are French.
- To refer to the possession of an object: This notebook is mine; The television is yours.
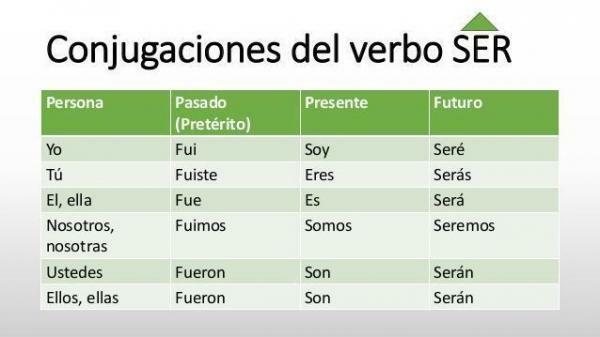
Image: Slideshare
Next, we explain what is the conjugation of the verb SER in Spanish, something different from the rest of the verbs of the second conjugation, since the verb SER it is one of the most irregular verbs that exist in Spanish.
Likewise, it is also one of the fundamental verbs of our language and it is convenient to be very clear about each of its different verb forms and to know how to differentiate the different modes.
INDICATIVE MODE
- Present: I am, you are, he is, we are, you are, they are.
- Perfect tense: I have been, you have been, he has been, we have been, you have been, they have been.
- Indefinite past tense: I was, you were, he was, we were, you were, they were.
- Imperfect preterite: I was, you were, he was, we were, you were, they were.
- Past perfect: I had been, you had been, he had been, we had been, you had been, they had been.
- Simple future: I will be, you will be, he will be, we will be, you will be, they will be.
- Composite future: I will have been, you will have been, he will have been, we will have been, you will have been, they will have been.
- Simple conditional: I would be, you would be, he would be, we would be, you would be, they would be.
- Conditional compound: I would have been, you would have been, he would have been, we would have been, you would have been.
SUBJUNCTIVE MODE
- Present: I am, you are, he is, we are, you are, they are.
- Imperfect past: I was or were, you were or were, he was or were, we were or were, you were or were, they were or were.
- Past perfect: I would have or would have been, you would have or would have been, he would have or would have been, we would have or would have been, you would have or would have been, they would have or would have been.
IMPERATIVE MODE
- Be, be, thirst, be



