SAUSSURE: language and speech
Linguistics is in charge of study human language applying different perspectives on it. The father of modern linguistics was Ferdinand de Saussure who thanks to his posthumous work General Linguistics Course He managed to establish different revolutionary theories on Linguistics and raise it to the field of Science. In this lesson from a TEACHER we will do a Saussure's summary: language and speech so that you can understand one of the most important dichotomies raised by the author.
Index
- Linguistics and Saussure's theories
- Dichotomy of language and speech
- What is speech (according to Saussure)
Linguistics and the theories of Saussure.
Linguistics is the science that is responsible for study human language applying different perspectives. This is mainly due to the historicist approach that began to take place in this discipline at the end of the 18th century. The scholars of the moment, begin to analyze Linguistics taking into account the modifications and mutations that the language suffered through time. Thus, and thanks to these revolutionary approaches, the
Comparative grammar which would include the Neogrammatists. These would be in charge of analyzing the evolution of the language over time in order to develop different theories and general laws that could be applied to all of them.After this revolution and within the Neogrammatists the figure of Ferdinand de Saussure (1857-1913) whose research was based on the study of signs in order to obtain concrete definitions of different concepts, in addition to providing analogies and examples based on games so that they were understood. On the other hand, he adopted a technical language for Linguistics making it become a Science.
During his long professional and research career, he created three courses on grammar, which were compiled after his death into his book General Linguistics Course in which there appears a premise that had not been given so far and that is that language is the object of study of Linguistics. To reach this conclusion, the author develops a theoretical framework that shows how language is composed and what it consists of, using a methodology based on different dichotomies. One of the most famous is that of language and speech.

Image: Slideshare
Dichotomy of language and speech.
It is the most important dichotomy of him within the work General Linguistics Course. Here the author states that language can be divided into two clearly differentiated parts and that goes on to define exhaustively. Thus, according to his theories, we can find that language is composed of:
- Language
- Speaks
What is language
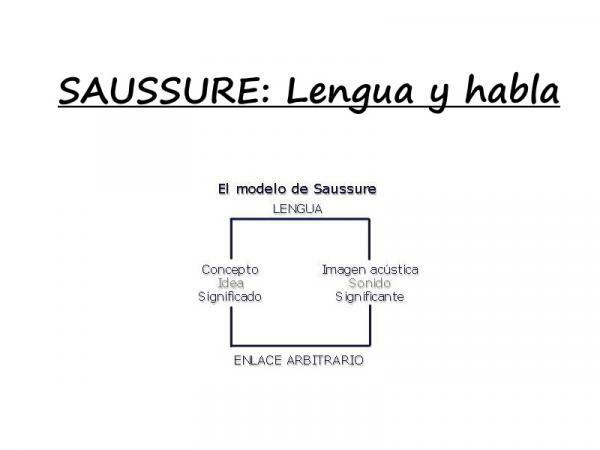
At this point is when the first dichotomy is established in which it is explained what the language. For Saussure this serves to express feelings and thoughts through the signs and is a universal human capacity. That is, all human beings have the ability of language to express their thoughts and feelings. At this point he raises his dichotomy in which he shows that language is nothing more than the conjunction of language and speech, the first of them with a social component and the second individual.
The union of this abstract part made up of language and the concrete part made up of speech are what make language arises, therefore, although both can be studied separately, they must be given at the same time so that there is language. In other words, if there is no speech and language, no language can exist.
What is language
The tongue is a abstract and cultural system. This, regardless of the will of the speakers, is composed of signs. That is, despite the fact that the speakers do not want to, every language is a culturally created and abstract system with its own signs. Thus, the language serves to express ideas to its speakers using their mental structures. Therefore, attending to his theories, we can extract a series of characteristics of the language:
- It is Social since this is a shared and common representation by a speaking community. In other words, language is knowledge that is shared and known by an entire speaking community.
- Because it is a knowledge that is found within the speakers, in their mental structures, and it is a concrete and not abstract knowledge, the language is called psychic.
- This makes the tongue passive since the information that the speaker already has is transformed by involuntary mental processes.
- Finally, language is a system of signs in which only the union of a concept with its acoustic image will be necessary, so that it could be said that language is homogeneous.

Image: Slideshare
What is speech (according to Saussure)
Speech is nothing but tool that allows you to communicate with others, is the realization of the language. This always has an intention and is individual in nature. We say this because for Saussure speech only makes individual events of each speaker participate in it.
Its characteristics include that speech is psychophysicalThis is because there must be a coding within the brain to transform ideas into words articulation in which the speech organs. That is to say, in addition to the psychic coding processes, the physical processes that allow us to articulate the different sounds.
He speaks is active, since the speaker is the one who decides when he wants to express or transmit an idea. He is the one who decides when he wants to take that knowledge that he has and produce it. Due to this, its psychophysical character and that it is variable, Saussure indicates that it is heterogeneous.
For the author, this dichotomy is one of the most important since it allows establishing that the object of study of Linguistics is language. This allows you to separate it from speech and develop both aspects of language independently.

Image: Slideplayer
If you want to read more articles similar to Saussure: Tongue and Speech - Summary, we recommend that you enter our category of Grammar and Linguistics.
Bibliography
SAUSSURE, F. General Linguistics Course. 4 ed., Buenos Aires, Argentina. Editorial Losada. 1961.



