What is the PRESENT of INDICATIVE

Image: Slideshare
The present indicative It is a very used verb tense in Spanish, for this reason in this lesson from a TEACHER we want to show you what it consists of, how it is formed, what it is used for and some examples so that you can easily identify it. First of all we must point out that it is one of the verb tenses more versatile since it can be used in many different situations acquiring different meanings. Take note of all the examples below so that you can easily identify it. Keep reading and you will discover what is the present indicative with examples.
The Present Indicative is one of the verb tenses in which the Spanish grammar is divided. It is one of the most used both in its written and oral expression and therefore, also one of the most useful in the language.
The Present Indicative in Spanish is used when the action that you want to express by the verb it is done at the moment in which it is spoken. That is, the action takes place at the moment the sender transmits the message.
But to know well what the Present Indicative is, we must focus on what it is used for. In addition to what was seen above, this verb tense is used to express certain actions in situations. In this other lesson we discover you what is Indicative mode.
Current facts
It is used when we want to show the facts or the actions that are being carried out at the moment of speaking. Let's see an example:
- This is my son.
- The house is messy.
- I'm talking on the phone.
Absolute truths
To express truths that they always happen. These truths cannot be questioned since they are proven, we see some examples to understand it better:
- The Sun rises in the East and sets in the West.
- The oil rubs into the water.
- Two times one is two.
Qualities of objects
It can be used when we want highlight the qualities of an object. To understand it better, here are some examples:
- This table is made of wood
- The menu costs 100 euros
- The chair is white and covered in leather.
Common situations
It is used when we want express situations that are carried out on a regular basis, that is to say that they are carried out normally but they do not have to be carried out at the moment in which it is spoken. In these examples you can see it very clearly:
- I work in a multinational.
- It takes me 50 minutes to get downtown.
- Ana sleeps 6 hours a day.
Time that an action has been going on
The Present Indicative is used when we want emphasize on time that an action is being carried out or being carried out:
- I have been working in this company since 1995.
- I have lived in the same house since I was born.
- He has been playing the piano since he was 8 years old.
Future actions
Can be used for describe future actions so that they are expressed with more emphasis by the issuer. We show you some examples to understand it better:
- Next week we are going to go hiking in the mountains.
- The party is on Friday at 10pm.
- You are discharged this afternoon
Periprastic future
The peripheral future It is formed using the verb to go or come and any other verb in the Present Indicative. She expresses future actions but to be fulfilled:
- My sister is going with them on a trip to Germany this vacation.
- On Saturday the air conditioning technician will come to check the installation.
- The toy will go straight to the storage room.
Actions of the past
They are actions that have happened in the past, but that are expressed in the Present Indicative to highlight their importance. Most of them are important facts, such as:
- Goya paints this painting for the Court.
- Columbus discovers America in 1942.
- The artist publishes his work for the first time in a local weekly.

Image: Slideplayer
The nature of the verb will show us how the Present Indicative should be constructed, that is, its formation will depend on whether it is regular or irregular.
Regular verbs
To form the Present indicative in regular verbs we must keep its root as an invariable part and add the following endings:
1st singular: I
- -or
- -or
- -or
2nd singular: You
- -ace
- -it is
- -it is
3rd singular: He, she, You
- -to
- -and
- -and
1st plural: We
- - let's
- -emos
- -we
2nd plural: You
- -you
- -you
- -is
3rd plural: they, they, You
- -an
- -on
- -on
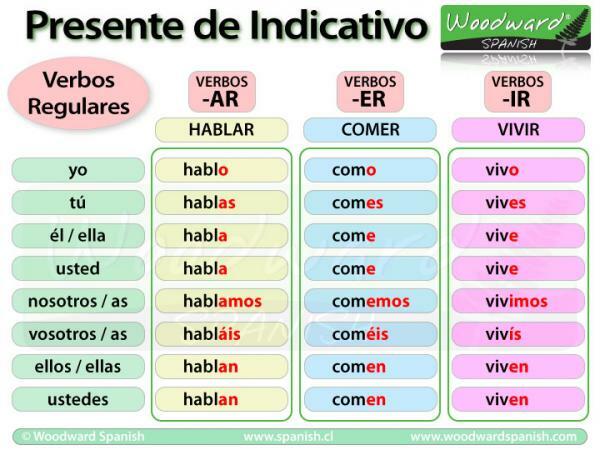
Let's see some examples of the Present Indicative. If we take as an example the verb sing. We will see that the root is qty- and this will be the one that must be combined with each of the people, remaining as follows:
- 1st singular: I sing
- 2nd singular: You sing
- 3rd singular: He, she, you sing
- 1st plural: We sing
- 2nd plural: You sing
- 3rd plural: they, they, you sing
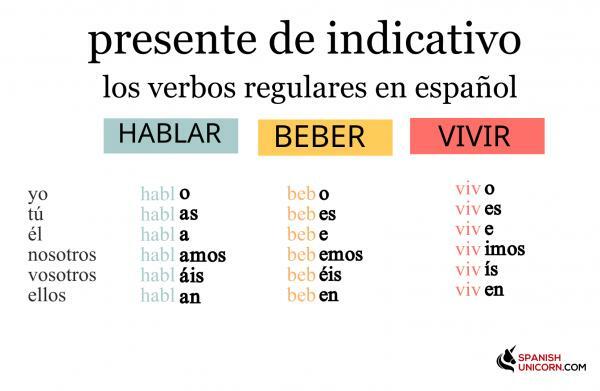
Image: Spanish Unicorn
These irregular verbs are the ones do not follow the above formula and therefore it must be conjugated in a different way. In some of them diphthongs are formed and in others a vowel change. These occur in all forms except the 1st and 2nd person plural.
- E becomes ie
- Or it becomes eu
- U becomes eu
- E becomes i
- U transform into uy
Examples of irregular verbs in Present Indicative
- Want
- Can
- Play
- Ask
- Conclude
- whatiero
- pEUdo
- jEUgo
- pido
- concloopsor
- whatiebeef
- pEUdes
- jEUgas
- pides
- concloopsit is
- whatiere
- pEUfrom
- jEUga
- pifrom
- concloopsand
- we want
- we can
- let's play
- we ask
- we conclude
- you want
- you can
- you play
- you ask
- you conclude
- whatieren
- pEUden
- jEUgan
- piden
- concloopson

![Sentences with verbs in INFINITIVE- [summary + examples!]](/f/81d0ba98daa57e7fa61b385068bf80f8.jpg?width=300&height=200)

