Word family: definition with examples
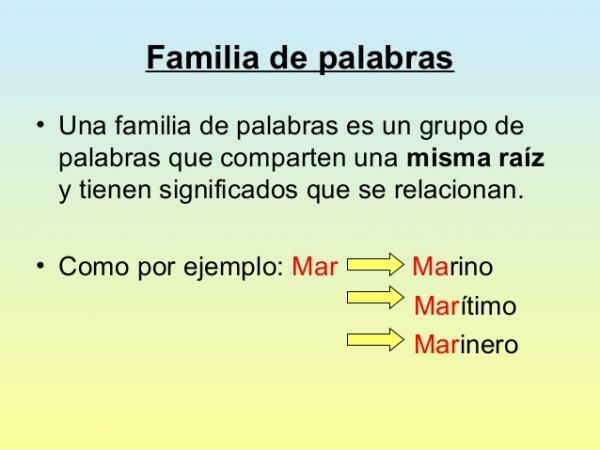
Image: Slideshare
In this lesson from a TEACHER we are going to explain what a word family consists of. Within the Spanish language we find words that are linked to each other through different semantic relationships; that is, words that share some significant feature. For example, we all know that a "greengrocer" is a place or an establishment where fruit is sold and bought. This is possible because the word "fruit shop" has part of its meaning in common with the base word, which is "fruit". We encourage you to continue reading this lesson to discover what is a word family!
As we have seen in the introduction to this lesson, words in Spanish are related to each other through different semantic links. The word family (or also known as lexical family) is a set of different words that share the same root; that is, they come from the same word.
This word from which the different families of Spanish words are formed is called primitive wordwhich is always the basis of every lexical family. In this way, we can say that the primitive word
contains all significant features necessary that then, little by little and in various ways, share with the rest of the words to give rise to the creation of the word family.As we have seen before, each word family always starts from a primitive word, which functions as the central axis of said lexical family. From it, we find other words with which it maintains links of meaning, but that each one of them presents some morphological alteration with respect to the meaning of the word primitive.
These words that share semantic characteristics with the primitive word are called derived words, which are all those words that, despite sharing some semantic feature with the word primitive, contain some nuances that add more meaning to the very meaning of the word primitive.
Image: Maestro San Blas
To understand a little better all the previous explanation, we are going to see it through some families of words. For example, the word "trust" is a primitive word because it is the one that contains all the semantic meaning that will later be common to the rest of derived words, either through prefixation (word creation process through which we add a prefix to a word to modify its meaning) or suffix (process parallel to prefixation, which consists of creating new words by adding a suffix).
Continuing with the previous example, once the primitive word has been established, which in this case is the verb "to trust", we have a series of words that derive from this same verb and that make up, together with it, a family of words. Some of the derived words are: "trust "," mistrust ", "confident", "trusting", "distrustful" or "distrustful".
Thus, another example would be the word family "box", which is the primitive word in this case, from which we can find all kinds of derived words that add some nuance or change of meaning with respect to the primitive. They are the following: "drawer", "box", "fit", "cashier", "box", "drawer", "drawer", "drawer", "box".
With this example we can see that the modifications experienced by the derived words arrive, in many times, to completely change the meaning, since a "box" is not the same as a "box". However, within the idea implied by the word "box" we do find common features with the primitive meaning of "box".



